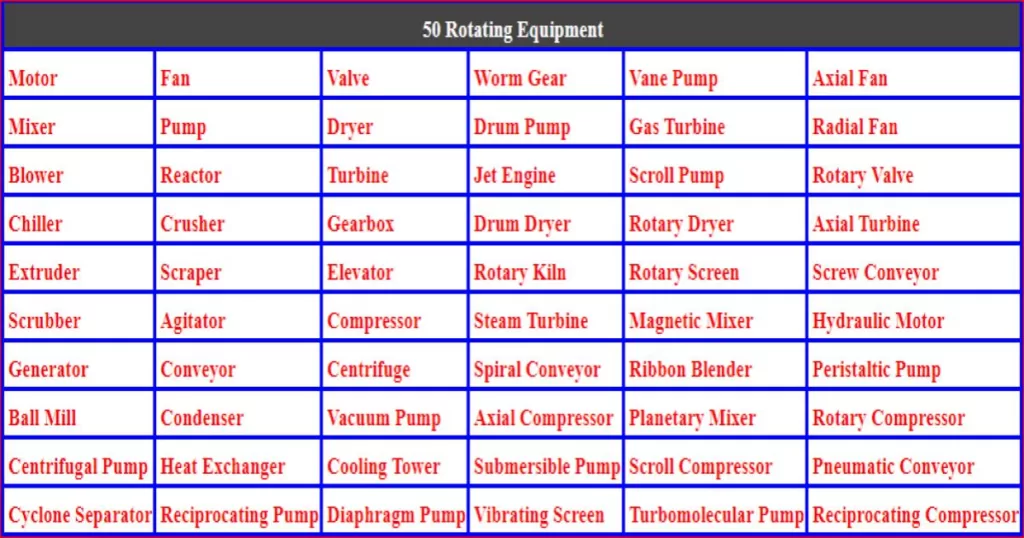
Wearing rings
Wearing rings, also known as wear rings, are components used in centrifugal pumps to minimize the leakage of fluid between the impeller and the pump casing. They are designed to provide a small running clearance between the impeller and the casing, which helps to improve pump efficiency and reduce wear on both components.
Here’s how wearing rings function in a pump system:
Impeller Wear Ring:
The impeller wear ring is a ring-shaped component mounted on the impeller. Its purpose is to reduce the axial and radial movement of the impeller, maintaining proper alignment and preventing contact between the impeller and the pump casing. By reducing the contact and minimizing the clearance, the impeller wear ring helps to improve the hydraulic efficiency of the pump and reduce internal recirculation losses.
Casing Wear Ring:
The casing wear ring, also called the stationary wear ring, is installed inside the pump casing. Its purpose is to provide a stationary surface against which the impeller wear ring rotates. The clearance between the impeller wear ring and the casing wear ring is maintained to a minimum, which reduces the leakage of fluid back into the impeller and improves pump performance.
The wearing rings are usually made of materials that have good resistance to wear and corrosion, such as stainless steel, bronze, or other suitable alloys. The materials are selected based on the specific application, taking into account factors such as the type of fluid being pumped, temperature, pressure, and the presence of any abrasive particles.
In some specialized pump applications where there are high pressures or hazardous fluids involved, stepped or double wearing rings may be used. These designs provide additional sealing and can withstand more demanding operating conditions.
It’s important to note that wearing rings require regular inspection and maintenance to ensure their proper functioning. Over time, due to wear and tear, the clearance between the wearing rings may increase, impacting pump efficiency. If the clearance becomes excessive, it may lead to increased leakage and decreased pump performance. Therefore, periodic replacement or adjustment of wearing rings is necessary to maintain optimal pump operation.
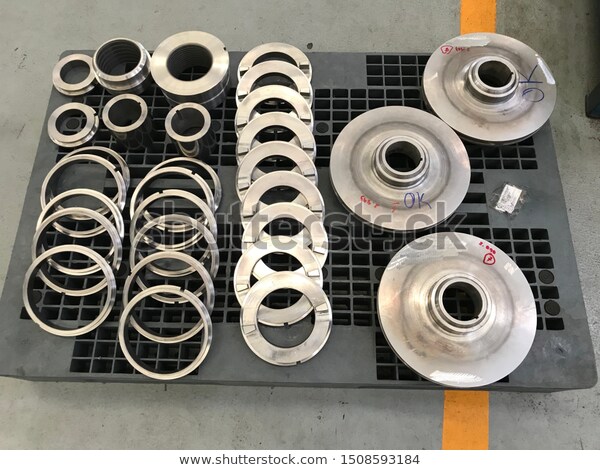 |
| Wearing |
What is the use of Wear rings in centrifugal pumps?
Wear rings, also known as wearing rings or impeller wear rings, are important components used in centrifugal pumps to reduce fluid leakage and improve pump performance. They serve the following purposes:
- Minimize Leakage: The primary function of wear rings is to minimize the leakage of fluid between the impeller and the pump casing. Centrifugal pumps work by creating a pressure differential that propels the fluid from the suction side to the discharge side. The wear rings create a small running clearance between the impeller and the casing, reducing the amount of fluid that can leak back from the discharge side to the suction side. This helps maintain efficiency and prevents recirculation losses.
- Improve Hydraulic Efficiency: By reducing the fluid leakage, wear rings contribute to improved hydraulic efficiency in centrifugal pumps. When there is minimal leakage, more fluid is directed to the desired flow path, resulting in higher pump efficiency. This translates into reduced energy consumption and improved overall performance.
- Protect Impeller and Casing: The wear rings act as sacrificial components, protecting the impeller and casing from direct contact and wear. As the impeller rotates, it comes in close proximity to the casing. The wear rings provide a small clearance that allows the impeller to rotate smoothly without touching the casing. This prevents metal-to-metal contact and reduces wear on both the impeller and the casing, prolonging their lifespan.
- Maintain Pump Performance: Over time, as the impeller and casing wear, the clearance between them can increase, leading to greater fluid leakage and decreased pump performance. Wear rings can be replaced or adjusted to restore the optimal running clearance. By maintaining the correct clearance, wear rings help ensure consistent pump performance and prevent efficiency losses.
- Reduce Vibration and Noise: The presence of wear rings helps reduce vibration and noise levels in centrifugal pumps. When the impeller and casing make direct contact, it can lead to increased vibration and noise, which may affect the pump’s operation and cause additional wear on the components. Wear rings dampen the vibrations and act as a buffer between the impeller and casing, resulting in smoother and quieter pump operation.
- Improve pump performance approx. (3-5 %) and also increase the life of pumps and impellers.
Why wear ring change in centrifugal pump?
Wear rings in centrifugal pumps may need to be changed or replaced for several reasons, including:
- Wear and Clearance Increase: Over time, wear rings can experience wear due to the continuous contact between the impeller and the wear ring itself. As wear progresses, the running clearance between the impeller and the wear ring may increase beyond the acceptable limits. This increased clearance can lead to increased fluid leakage and reduced pump efficiency. Changing the wear rings helps restore the proper running clearance and maintain optimal pump performance.
- Reduced Pump Efficiency: As wear rings wear down and the clearance between the impeller and the casing increases, fluid can leak back from the discharge side to the suction side. This recirculation of fluid reduces the pump’s hydraulic efficiency, as the leaked fluid does not contribute to the desired flow. By replacing worn wear rings, the clearance is reduced, minimizing leakage and improving the pump’s overall efficiency.
- Preventive Maintenance: Wear rings are often replaced as part of a preventive maintenance program to ensure reliable pump operation. Regular inspection and replacement of wear rings can help prevent unexpected failures, downtime, and costly repairs. By proactively replacing wear rings before they cause significant performance issues, pump reliability and efficiency can be maintained.
- Component Damage: If wear rings are not replaced when necessary, the increased clearance between the impeller and the casing can lead to more severe damage to the impeller and casing surfaces. This can result in reduced pump efficiency, increased vibration, and potential failure of other pump components. By replacing worn wear rings promptly, the risk of damage to other components is minimized.
- Change in Operating Conditions: If there is a change in the operating conditions of the pump, such as increased pressure, temperature, or fluid characteristics, the existing wear rings may no longer be suitable. Different operating conditions may require wear rings made from different materials or with specific design features. Changing the wear rings to ones better suited for the new operating conditions ensures optimal pump performance and longevity.
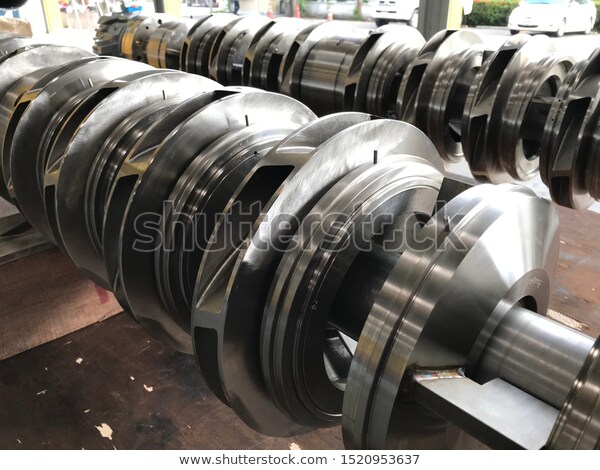 |
| Wearing clearance |
Types of wear ring
There are different types of wear rings used in centrifugal pumps, each designed to suit specific applications and operating conditions. Here are some common types of wear rings:
- Single Wear Ring: The single wear ring configuration is the most basic and commonly used type. It consists of a single wear ring installed either on the impeller or inside the pump casing. The wear ring provides a running clearance between the impeller and the casing to minimize fluid leakage and reduce wear.
- Double Wear Ring: Double wear rings consist of two wear rings, one installed on the impeller and the other inside the pump casing. This configuration provides an additional sealing barrier and helps further reduce fluid leakage. Double wear rings are often used in pumps handling high-pressure fluids or in applications with stringent leakage requirements.
- Stepped Wear Ring: Stepped wear rings have a stepped profile, where the diameter of the wear ring increases in steps. This design is used in applications with high pressure or where there is a risk of cavitation. The stepped profile helps to reduce the pressure drop across the wear ring and mitigate the effects of cavitation, enhancing pump performance and reliability.
- Tapered Wear Ring: Tapered wear rings have a tapered profile, meaning the thickness of the wear ring varies along its circumference. This design allows for a more gradual reduction in clearance as the fluid flows between the impeller and the casing. Tapered wear rings are beneficial in applications where there is a potential for abrasive particles or solids in the fluid, as they help minimize the risk of clogging or blockage.
- Split Wear Ring: Split wear rings are designed to facilitate easier installation and replacement. They are manufactured in two or more segments that can be assembled around the impeller or inserted into the pump casing. Split wear rings eliminate the need to remove the impeller or dismantle the entire pump during wear ring replacement, resulting in significant time and cost savings during maintenance.
- Composite Wear Ring: Composite wear rings are made from non-metallic materials, such as carbon-filled PTFE (polytetrafluoroethylene) or other high-performance polymers. These materials offer excellent resistance to wear, corrosion, and chemical attack. Composite wear rings are lightweight, provide good thermal stability, and can be used in a wide range of applications.
What type of tools do you use in installation of wear ring?
Metrology refers to the science of measurement and the techniques used for precise measurement. In the case of wear rings, metrology plays an important role in ensuring accurate measurements of dimensions, clearances, and tolerances. Here are some commonly used metrology techniques in the measurement of wear rings:
- Calipers: Calipers are handheld measuring tools used to measure the outer diameter, inner diameter, and thickness of wear rings. Vernier calipers or digital calipers can provide precise measurements and are commonly used for quick and straightforward measurements.
- Micrometers: Micrometers are precise instruments used to measure dimensions with high accuracy. They can be used to measure the thickness of wear rings and provide measurements in micrometers (μm) or millimeters (mm). Outside micrometers and inside micrometers can be employed depending on the dimension being measured.
- Coordinate Measuring Machine (CMM): CMM is a sophisticated measuring device used for accurate and comprehensive dimensional measurement. It uses a probe to measure multiple points on the surface of a wear ring and creates a digital representation of the measured dimensions. CMMs can measure complex geometries and provide detailed information about the wear ring’s form, profile, and tolerances.
- Optical Profilometers: Optical profilometers use light interference patterns to measure surface profiles and roughness. They can be used to assess the surface finish and wear patterns on wear rings. By scanning the wear ring’s surface, optical profilometers generate 3D representations and provide detailed information about wear characteristics.
- Optical Comparators: Optical comparators use a projected image of a wear ring onto a screen, enabling accurate measurement and comparison of dimensions. They are particularly useful for checking the profile and form of wear rings against established standards or specifications.
- Surface Roughness Testers: Surface roughness testers are instruments used to measure the roughness of wear ring surfaces. They employ either contact or non-contact methods to assess the roughness parameters, such as Ra (average roughness) or Rz (maximum peak-to-valley height). This information helps evaluate the wear ring’s surface quality and its impact on performance.
- Profilometers: Profilometers are instruments used to measure the profile of wear rings, including their surface contours, shapes, and deviations from ideal geometry. They utilize a stylus or non-contact methods like laser scanning to capture the wear ring’s profile data.
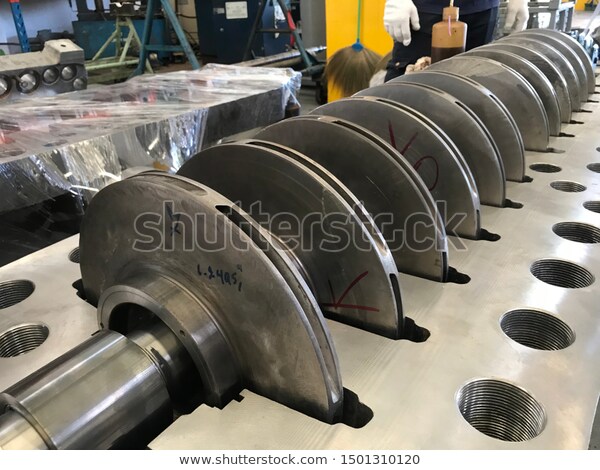 |
| Wearing ring materials |
How to replace wearing in centrifugal pump?
Replacing the wearing rings in a centrifugal pump typically involves the following steps:
- Preparation:
- Ensure the pump is shut down and isolated from the power source.
- Release any pressure or residual fluid in the system according to proper safety procedures.
- Prepare the necessary tools and equipment, such as replacement wearing rings, gaskets, sealant (if required), and measuring instruments.
- Disassembly:
- Remove the pump casing cover or volute to access the impeller and wearing rings.
- Carefully remove the impeller from the pump shaft, following the manufacturer’s instructions and any specific precautions.
- Inspect the existing wearing rings for wear, damage, or excessive clearance.
- Removal of Existing Wearing Rings:
- Depending on the pump design, the wearing rings may be press-fit or held in place by screws or retaining devices.
- If the wearing rings are press-fit, use appropriate tools like bearing pullers or hydraulic presses to carefully remove them.
- If there are retaining screws or devices, unscrew or release them to remove the wearing rings.
- Cleaning and Inspection:
- Thoroughly clean the impeller, casing, and surrounding areas to remove any debris, dirt, or residue.
- Inspect the impeller and casing for any signs of damage, excessive wear, or corrosion. Address any issues before proceeding with the replacement.
- Installation of New Wearing Rings:
- Ensure the new wearing rings are of the correct size, material, and design as recommended by the pump manufacturer or based on specific application requirements.
- If the wearing rings are press-fit, carefully align and position them in their respective locations. Use appropriate tools and techniques to press them into place.
- If retaining screws or devices are used, follow the manufacturer’s instructions to securely fasten the wearing rings in position.
- Reassembly:
- Reinstall the impeller onto the pump shaft, ensuring proper alignment with the wearing rings.
- Replace any gaskets or seals that were removed during disassembly, applying sealant if necessary.
- Carefully reinstall the pump casing cover or volute, ensuring proper alignment and sealing.
- Testing and Final Checks:
- Ensure all connections, bolts, and fasteners are tightened to the manufacturer’s specifications.
- Conduct a visual inspection to verify that the wearing rings are properly seated and aligned.
- Prime the pump and start it up to check for smooth operation, ensuring there are no abnormal vibrations, noises, or leaks.
- Monitor the pump’s performance and verify that the wearing rings are functioning correctly, with reduced leakage and improved efficiency.
2nd process of installation
To replace the wearing ring in a centrifugal pump, follow the steps outlined below, ensuring proper safety precautions are taken:
- Loosen Set Screws:
- Identify the set screws that secure the wearing ring to the pump casing.
- Carefully loosen all the set screws using an appropriate tool.
- Take care not to damage the set screws or the casing during this process.
- Remove Wearing Ring from Casing:
- Use a soft-faced hammer or mallet to gently tap on the inside of the wearing ring near the casing assembly.
- Apply gradual and controlled force to try and pull the wearing ring out.
- If the wearing ring does not come out easily, proceed to the next step.
- Weld Steel Rod to Wearing Ring (For Stubborn Cases):
- Take a steel rod that is nearly the same diameter as the inside of the wearing ring.
- Weld both ends of the steel rod to the inside of the wearing ring.
- Use a grinding machine or cutting wheel to make small cuts on the opposite side of the weld, creating weak points.
- Break Wearing Ring Using Hammer:
- Gradually and carefully strike the rod with hammers, applying force to break the wearing ring.
- The wearing ring should break from the weak points created by the cuts.
- Once broken, the wearing ring can be easily pulled out.
- Repeat this process for the wearing ring on the impeller, omitting the step of welding the rod.
- Alternative Method Using Drill Machine:
- If set screws cannot be loosened, use a drill machine with a drill bit that matches the outside diameter of the set screw.
- Drill a hole between the casing and wearing ring at the location of the set screw.
- Drill until the set screw becomes detached or compromised, allowing for easy removal of the wearing ring from the impeller.
- Heat or Cool Method:
- If other methods fail, consider applying heat or cooling techniques.
- Apply heat to the wearing ring using oil, a torch, or an appropriate heating device to expand the metal and facilitate removal.
- Alternatively, cool the wearing ring using ice or liquid nitrogen to contract the metal and loosen its grip for easier extraction.
Always exercise caution and follow appropriate safety procedures when using heat or cooling methods.
Remember to consult the pump manufacturer’s guidelines, technical manuals, and safety instructions for the specific pump model you are working with.
How do you measure ring clearance between wearing rings?
Measuring the ring clearance between wear rings in a centrifugal pump involves the following step-by-step guide:
- Prepare for Measurement:
- Ensure the pump is shut down and isolated from the power source.
- Make sure the pump casing cover or volute is removed to access the wear rings.
- Gather the necessary measuring tools, such as micrometers, feeler gauges, or dial indicators.
- Clean the Surfaces:
- Thoroughly clean the surfaces of the wear rings and the mating components to remove any dirt, debris, or residue that could affect the accuracy of the measurement.
- Use a suitable cleaning agent and ensure the surfaces are dry before proceeding.
- Select the Measuring Technique:
- Choose a suitable measuring technique based on the available tools and the design of the wear rings.
- Common techniques include using micrometers, feeler gauges, or dial indicators.
- Using Micrometers:
- Use an outside micrometer to measure the outer diameter (OD) of the wear ring and the inner diameter (ID) of the casing or impeller.
- Take multiple measurements at different points around the circumference of the wear ring and record the values.
- Calculate the ring clearance by subtracting the measured OD from the measured ID.
- Repeat the measurement on both the impeller wear ring and the casing wear ring.
- Using Feeler Gauges:
- Insert a feeler gauge of known thickness into the ring clearance gap between the wear ring and the mating component.
- Choose a feeler gauge that is thin enough to fit into the gap but thick enough to provide a reliable measurement.
- Gradually increase the thickness of the feeler gauge until there is a slight resistance when sliding it between the surfaces.
- Record the thickness of the feeler gauge, which represents the ring clearance.
- Repeat the measurement on both the impeller wear ring and the casing wear ring.
- Using Dial Indicators:
- Mount a dial indicator with an appropriate holder or fixture to measure the movement of the wear ring.
- Position the dial indicator’s contact point against the wear ring surface.
- Apply a slight force to compress the wear ring towards the mating component and zero the dial indicator.
- Gradually release the force and observe the movement of the dial indicator’s needle.
- The movement of the needle represents the ring clearance.
- Repeat the measurement on both the impeller wear ring and the casing wear ring.
- Record and Evaluate the Measurements:
- Document the measurements obtained for each wear ring.
- Compare the measured ring clearance values to the manufacturer’s specifications or recommended tolerances.
- If the measured clearance is outside the acceptable range, consider replacing the wear rings to ensure proper pump performance and efficiency.
How wear ring is fitted to impeller?
The process of fitting or installing a wear ring to an impeller in a centrifugal pump typically involves the following steps:
- Prepare for Installation:
- Ensure the pump is shut down and isolated from the power source.
- Make sure the impeller is accessible by removing any pump casing covers or volutes.
- Gather the necessary tools, including the new wear ring, lubricant (if required), and any recommended installation aids.
- Inspect the Impeller and Wear Ring:
- Thoroughly inspect the impeller and wear ring for any signs of damage, wear, or corrosion.
- Ensure the wear ring is of the correct size, material, and design specified by the pump manufacturer or based on application requirements.
- Lubricate the Wear Ring:
- If recommended by the manufacturer, apply a thin layer of lubricant or compatible sealant to the outer surface of the wear ring.
- Lubrication can assist in the ease of installation and ensure proper sealing.
- Position the Wear Ring:
- Orient the wear ring so that the correct side faces the impeller.
- The wear ring should have a beveled edge or chamfer on one side, which should face the impeller.
- Align and Fit the Wear Ring:
- Align the wear ring with the corresponding groove or recess in the impeller.
- Carefully slide or press the wear ring into the groove, ensuring it is seated properly.
- Apply even pressure around the circumference of the wear ring to ensure uniform fitment.
- Avoid excessive force that could cause damage to the impeller or wear ring.
- Check the Fit and Clearance:
- Verify that the wear ring is seated flush and evenly against the impeller surface.
- Check the ring clearance between the wear ring and the impeller to ensure it meets the manufacturer’s specifications or recommended tolerances.
- Use appropriate measuring techniques, such as micrometers or feeler gauges, to confirm the clearance if necessary.
- Reassemble the Pump:
- Once the wear ring is correctly installed on the impeller, proceed to reassemble the pump.
- Replace any gaskets, seals, or components that were removed during the disassembly process.
- Follow the manufacturer’s instructions to secure the impeller and reattach the pump casing covers or volutes.
- Perform Testing and Verification:
- Prime the pump and start it up to ensure proper operation.
- Monitor the pump’s performance, checking for any abnormal vibrations, noises, or leaks.
- Verify that the wear ring is functioning correctly, providing improved sealing and reduced leakage between the impeller and the casing.
How do you get a wearing ring off?
This is already mentioned and discussed in the above section you can check from here paragraph. you can check more details by following the links. wearing in other source