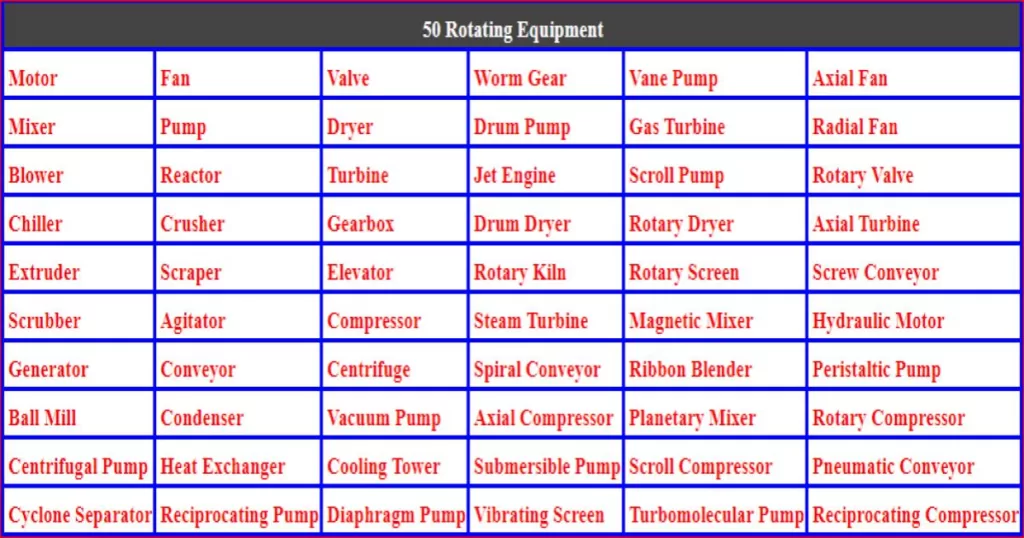
Type of pumps
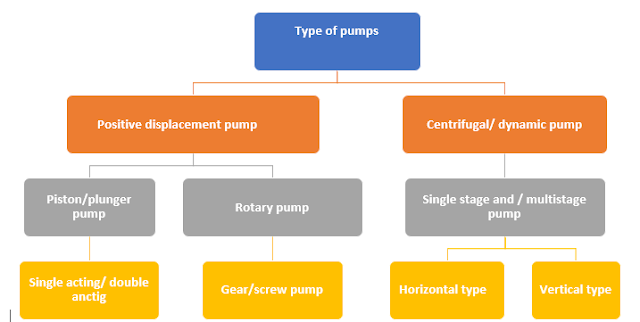
Classification of pump
- Positive displacement pump
- Centrifugal pump (Dynamic pump)
Centrifugal pump
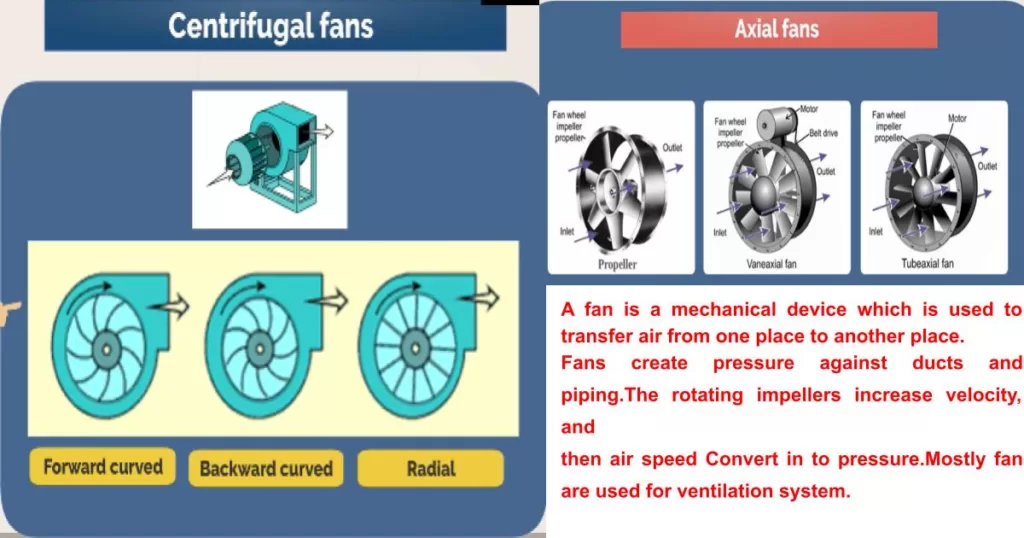
Centrifugal pump is a mechanical device. They are the most commonly used type of pump because they are efficient, reliable, and easy to use. They move liquid or gas by using an impeller that rotates inside a chamber to create pressure. The rotating action forces liquid through the outlet as more liquid is pulled from the inlet side. This pump can be used for a wide range of applications, from moving small volumes of liquids over short distances to transferring large amounts of fluids at great distances. These type of pump also use in water treatment plants.
Positive displacement pump
- Rotary pump
- Reciprocating pump
- Screw pump
- Lobe pump
- Piston pump
- Plunger type pump
- Diaphragm pump
- Single acting reciprocating pump
- Multi acting reciprocating pump
Sure, here’s a list of types of pumps commonly used in various industries and its introduction:
- Centrifugal Pumps
- Positive Displacement Pumps
- Diaphragm Pumps
- Gear Pumps
- Screw Pumps
- Vane Pumps
- Peristaltic Pumps
- Piston Pumps
- Progressive Cavity Pumps
- Regenerative Turbine Pumps
- Axial Flow Pumps
- Mixed Flow Pumps
- Eductor-Jet Pumps
- Lobe Pumps
- Magnetic Drive Pumps
- Multi-Stage Pumps
- Rotary Lobe Pumps
- Submersible Pumps
- Vertical Turbine Pumps
- Air Operated Double Diaphragm (AODD) Pumps
Diaphragm Pumps:
Diaphragm pumps use a flexible diaphragm to create pressure and flow. The diaphragm is typically made of rubber or thermoplastic material, and is moved back and forth by a mechanism to create suction and discharge strokes. They are commonly used in applications that require low flow rates and high pressures, as well as in applications where the fluid being pumped is corrosive or abrasive. Diaphragm pumps can handle temperatures ranging from -40°C to 200°C and pressures ranging from 0.2 bar to 7 bar. They are often used in the chemical, pharmaceutical, and food and beverage industries. One of the main benefits of diaphragm pumps is their ability to handle a wide range of fluids, including viscous and abrasive liquids.
Gear Pumps:
Gear pumps use meshing gears to create flow. As the gears rotate, they create pockets of fluid that are carried from the inlet to the outlet of the pump. They are commonly used in applications that require low flow rates and high pressures, as well as in applications where a constant flow rate is required. Gear pumps can handle temperatures ranging from -40°C to 200°C and pressures ranging from 0.1 bar to 350 bar. They are often used in the chemical, pharmaceutical, and food and beverage industries. One of the main benefits of gear pumps is their simplicity, as they have only two moving parts and require minimal maintenance.
- Internal gear pump
- External gear pump
Screw Pumps:
Screw pumps use rotating screws to create flow. The screws mesh together to trap and move fluid from the inlet to the outlet of the pump. They are commonly used in applications that require high flow rates and high pressures. Screw pumps can handle temperatures ranging from -40°C to 300°C and pressures ranging from 0.5 bar to 100 bar. They are often used in the oil and gas, chemical, and food and beverage industries. One of the main benefits of screw pumps is their ability to handle high viscosity fluids with ease.
Vane Pumps:
Vane pumps use sliding vanes to create flow. The vanes move in and out of slots in a rotating rotor, creating a pumping action. They are commonly used in applications that require low to moderate flow rates and moderate pressures. Vane pumps can handle temperatures ranging from -20°C to 200°C and pressures ranging from 0.5 bar to 25 bar.
Peristaltic Pumps:
Peristaltic pumps are positive displacement pumps that use rotating rollers to compress and release a flexible tube, creating a vacuum and drawing fluid into the tube. They are capable of pumping a wide range of fluids, including abrasive and viscous fluids, and are often used in applications where contamination or product degradation must be avoided. They are also commonly used in the medical and pharmaceutical industries. The operating temperature and pressure range of peristaltic pumps depends on the material of the tubing used. They can handle pressures up to 100 psi and temperatures up to 212°F (100°C).
Piston Pumps:
Piston pumps are positive displacement pumps that use reciprocating pistons to move fluids through a cylinder. They are commonly used in applications that require high pressures and flow rates, such as oil and gas production, power generation, and chemical processing. Piston pumps can handle pressures up to 10,000 psi and temperatures up to 500°F (260°C). There is one popular types of piston pump is r902504306 bosch rexroth piston pump.
Progressive Cavity Pumps:
Progressive cavity pumps are positive displacement pumps that use a rotating screw or helical rotor to move fluids through a stator. They are commonly used in applications that require high viscosity or shear-sensitive fluids, such as food processing, wastewater treatment, and oil and gas production. The operating temperature range of progressive cavity pumps is typically between -40°F (-40°C) and 300°F (149°C), and they can handle pressures up to 6,000 psi.
Regenerative Turbine Pumps:
Regenerative turbine pumps are centrifugal pumps that use a rotor with multiple vanes to generate high pressure and flow rates. They are commonly used in applications that require high pressure, such as refrigeration and air conditioning systems, and can handle pressures up to 2,000 psi and temperatures up to 500°F (260°C).
Axial Flow Pumps:
Axial flow pumps are centrifugal pumps that use a propeller-like impeller to move fluid in a axial direction. They are commonly used in applications that require high flow rates, such as flood control, irrigation, and cooling systems. Axial flow pumps can handle pressures up to 100 psi and temperatures up to 200°F (93°C).
Mixed Flow Pumps:
Mixed flow pumps are centrifugal pumps that combine the features of radial and axial flow pumps to generate a hybrid flow pattern. They are commonly used in applications that require high flow rates and moderate pressure, such as water supply systems and irrigation. Mixed flow pumps can handle pressures up to 200 psi and temperatures up to 200°F (93°C).
Eductor-Jet Pumps:
Working principle: Eductor-jet pumps use a high-velocity jet of fluid to create suction and entrain another fluid or gas. They do not have any moving parts. Operating temperature and pressure range: They can handle temperatures from -20°C to 400°C and pressures up to 1,500 psi. Applications and benefits: Eductor-jet pumps are commonly used in the chemical, petrochemical, and process industries for mixing, pumping, and circulating fluids. They are easy to install, have low maintenance requirements, and can handle fluids with high solids content or viscosity.
Lobe Pumps:
Working principle: Lobe pumps use two or more rotating lobes to transfer fluid from the inlet to the outlet. The fluid is trapped between the lobes and the pump casing and is transported around the casing to the discharge port. Operating temperature and pressure range: They can handle temperatures up to 150°C and pressures up to 20 bar. Applications and benefits: Lobe pumps are commonly used in the food, beverage, and pharmaceutical industries because they can handle delicate fluids without damaging them. They are also suitable for transferring fluids with high solids content or viscosity, and are easy to clean and maintain.
Magnetic Drive Pumps:
Working principle:
Magnetic drive pumps use a magnetic coupling to transfer power from the motor to the impeller. The impeller is enclosed in a hermetically sealed casing, which eliminates the need for a shaft seal. Operating temperature and pressure range: They can handle temperatures up to 150°C and pressures up to 20 bar. Applications and benefits: Magnetic drive pumps are commonly used in the chemical, pharmaceutical, and semiconductor industries because they are leak-proof and do not emit any harmful vapors. They are also suitable for handling corrosive or hazardous fluids.
Multi-Stage Pumps:
Working principle:
Multi-stage pumps use multiple impellers to increase the pressure of the fluid being pumped. Each impeller is connected in series to the previous impeller. Operating temperature and pressure range: They can handle temperatures up to 150°C and pressures up to 40 bar. Applications and benefits: Multi-stage pumps are commonly used in water supply, irrigation, and fire-fighting systems because they can generate high pressure and flow rates. They are also used in the oil and gas industry for injection, boosting, and offshore applications.

Rotary Lobe Pumps:
Working principle:
Rotary lobe pumps use two or more rotating lobes to transfer fluid from the inlet to the outlet. The fluid is trapped between the lobes and the pump casing and is transported around the casing to the discharge port. Operating temperature and pressure range: They can handle temperatures up to 150°C and pressures up to 20 bar. Applications and benefits: Rotary lobe pumps are commonly used in the food, beverage, and pharmaceutical industries because they can handle delicate fluids without damaging them. They are also suitable for transferring fluids with high solids content or viscosity, and are easy to clean and maintain.
Submersible Pumps:
Working principle:
Submersible pumps are designed to be immersed in the fluid being pumped. They use a hermetically sealed motor to drive the impeller, and are cooled by the fluid being pumped. Operating temperature and pressure range: They can handle temperatures up to 60°C and pressures up to 20 bar. Applications and benefits: Submersible pumps are commonly used in wastewater treatment, drainage, and mining applications because they can operate in harsh and dirty environments. They are also easy to install and require minimal maintenance.
Vertical Turbine Pumps:
Introduction:
Vertical Turbine Pumps are a type of centrifugal pump that is designed to operate in a vertical orientation, with the motor located above the pump bowl assembly. They are commonly used for pumping water from deep wells or other underground sources.
Working Principle:
Vertical Turbine Pumps use a spinning impeller to create a centrifugal force that moves water up the pump shaft and out of the discharge port. The impeller is typically driven by a vertical electric motor that is connected to the pump through a long shaft.
Operating Temperature and Pressure Range:
Vertical Turbine Pumps can operate at a wide range of temperatures and pressures, depending on the materials used in the pump construction. They are commonly used in applications that require high flow rates and high heads.
Applications and Benefits:
Vertical Turbine Pumps are commonly used in municipal water supply systems, agricultural irrigation systems, and industrial applications such as cooling towers and fire protection systems. They offer several benefits over other types of pumps, including high efficiency, low maintenance, and long service life.
Air Operated Double Diaphragm (AODD) Pumps:
Introduction:
Air Operated Double Diaphragm (AODD) Pumps are a type of positive displacement pump that uses compressed air to move fluid through the pump. They are commonly used for pumping fluids that are viscous, abrasive, or contain solids.
Working Principle:
AODD Pumps use two flexible diaphragms that are connected to a common shaft. Compressed air is used to alternately push and pull the diaphragms, causing the fluid to be drawn into and discharged from the pump. The pumping action is similar to that of a reciprocating engine.
Operating Temperature and Pressure Range:
AODD Pumps can operate at a wide range of temperatures and pressures, depending on the materials used in the pump construction. They are commonly used in applications that require low to medium flow rates and low to medium heads.
Applications and Benefits:
AODD Pumps are commonly used in chemical processing, food and beverage processing, wastewater treatment, and other industrial applications. They offer several benefits over other types of pumps, including the ability to handle a wide range of fluids, easy maintenance, and the ability to run dry without damaging the pump.