RCM Maintenance Definitions
RCM (Reliability Centered Maintenance) is a maintenance strategy that focuses on maximizing the reliability of equipment and minimizing the risk of failure. It is a systematic approach to maintenance that is based on identifying and prioritizing maintenance tasks based on the risk of equipment failure. And By assessing risks and utilizing preventative maintenance tasks, RCM can help optimize engine performance and ensure that machines are running optimally.
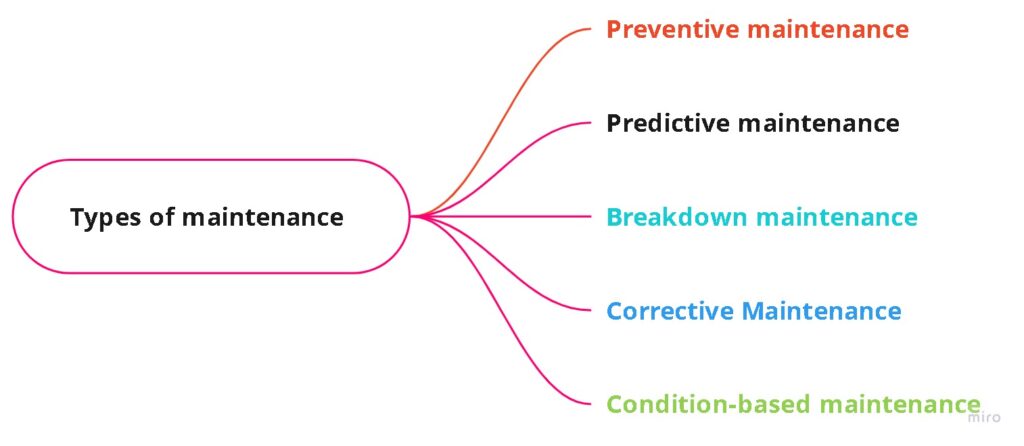
Types of RCM Maintenance
- Reactive Maintenance: This type of maintenance is performed after a failure occurs. It is also known as “breakdown maintenance”.
- Preventive Maintenance: This type of maintenance is performed on a regular basis to prevent failures from occurring. It is also known as “scheduled maintenance”.
- Predictive Maintenance: This type of maintenance is performed using advanced tools and techniques to predict when failures are likely to occur.
- Proactive Maintenance: This type of maintenance is performed to address potential problems before they occur. It is also known as “reliability-centered maintenance”.
Understand the Principals of RCM Maintenance
It is important to understand the fundamentals of RCM maintenance before implementing any preventative maintenance tasks. At its most basic, RCM involves identifying all potential failure modes of an equipment and then choosing cost-effective solutions based on risk assessment. This means that as part of your strategy, you should analyze the time between breakdowns, consider how severe the consequences could be if a failure were to occur, and conduct Stress/Life Analysis when necessary. Doing so will help ensure that the right level of maintenance is applied at the right time.
Analyze and Identify Critical Assets
To use the principles and techniques of RCM, it is important to first analyze and identify all the critical assets in your facility and their vital components. This should be done systematically so that all maintenance activities can target the right consequences at any given time. A proper analysis will include steps like data collection, event assertion, cause analysis, consequence ranking and risk evaluation. This process allows you to anticipate failure modes and prioritize maintenance tasks quickly while also helping avoid costs incurred by unnecessary interventions.
Implement Optimized Maintenance Tasks
After identifying and understanding the potential failures that your equipment may experience, the next step is to develop scheduled maintenance strategies for each item. In some cases, existing tasks may be able to be optimized for more effective results. Conversely, interventions may need to be established if current practices aren’t quite up-to-date or effective. By using RCM data and guidelines, you can formulate maintenance strategies that increase reliability while still preserving freshness of components.
Monitor and Improve Your Equipment Performance Using KPIs and Reports
Reliability-Centered Maintenance (RCM) isn’t just about developing maintenance strategies; it is also about evaluating the performance of your equipment. To do this properly, you need to develop key performance indicators (KPIs) and generate reports regularly. This allows you to monitor the performance of your machinery as well as determine which areas are performing poorly or not up to par. It will also help you identify factors that impact reliability by providing important data points and trends. With this information, you can develop action plans accordingly and take steps towards improving the health of your equipment.
Application and Importance of RCM Maintenance:
RCM Maintenance can be applied to any industry or equipment that requires maintenance. The main importance of RCM maintenance is to increase equipment reliability, reduce maintenance costs, and improve safety. By focusing on the critical components and failure modes of equipment, RCM maintenance helps to prioritize maintenance tasks, ensure that the right maintenance is performed at the right time, and avoid unnecessary maintenance.
Method of RCM Maintenance:
The RCM maintenance process typically involves the following steps:
- Identify the equipment to be maintained.
- Define the functions and performance standards of the equipment.
- Identify the potential failure modes of the equipment.
- Determine the consequences of each failure mode.
- Prioritize the failure modes based on their consequences.
- Identify maintenance tasks to mitigate the risks associated with each failure mode.
- Determine the frequency and type of maintenance required for each task.
- Implement the maintenance plan and monitor its effectiveness.
Calculation for RCM Maintenance:
- There are several formulas used in RCM maintenance. Some of the most common ones are:
- Availability = (Total Time – Downtime) / Total Time
- Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF) = Total Operating Time / Number of Failures
- Mean Time to Repair (MTTR) = Total Downtime / Number of Repairs
Example of RCM Maintenance:
Suppose a company has a production line with a critical machine that must be kept operational at all times. The RCM maintenance process for this machine might involve the following steps:
- Identify the equipment to be maintained: Critical machine in the production line.
- Define the functions and performance standards of the equipment: The machine must operate continuously to meet production requirements.
- Identify the potential failure modes of the equipment: motor failure, bearing failure, and electrical failure.
- Determine the consequences of each failure mode: Production downtime, product quality issues, and safety risks.
- Prioritize the failure modes based on their consequences: Electrical failure has the highest consequence, followed by bearing failure and motor failure.
- Identify maintenance tasks to mitigate the risks associated with each failure mode: Regular inspections, electrical testing, and bearing lubrication.
- Determine the frequency and type of maintenance required for each task: Electrical testing should be done monthly, bearing lubrication every 3 months, and inspections every 6 months.
- Implement the maintenance plan and monitor its effectiveness: Schedule the maintenance tasks and monitor the machine’s performance to ensure that the maintenance plan is effective in preventing failures.
RCM maintenance how to apply on centrifugal pump
RCM maintenance can be applied to centrifugal pumps to help improve their reliability and minimize the risk of failure. The following steps can be taken when applying RCM maintenance to a centrifugal pump:
- Identify the equipment to be maintained: In this case, the centrifugal pump is the equipment to be maintained.
- Define the functions and performance standards of the equipment: The centrifugal pump is used to move fluids from one location to another. It must operate efficiently and reliably to meet production or process requirements.
- Identify the potential failure modes of the equipment: Common failure modes for centrifugal pumps include bearing failure, seal failure, impeller damage, and motor failure.
- Determine the consequences of each failure mode: The consequences of centrifugal pump failure can include production downtime, product quality issues, safety risks, and increased maintenance costs.
- Prioritize the failure modes based on their consequences: Failure modes should be prioritized based on the severity of their consequences. For example, bearing failure may have a lower consequence than seal failure because it is easier and quicker to repair.
- Identify maintenance tasks to mitigate the risks associated with each failure mode: For example, regular inspections, vibration monitoring, lubrication, and seal replacement can be performed to prevent bearing or seal failure. Impeller inspection and repair can be performed to prevent impeller damage. Motor inspection and testing can be performed to prevent motor failure.
- Determine the frequency and type of maintenance required for each task: The frequency and type of maintenance required will depend on the specific pump and its operating conditions. For example, vibration monitoring may need to be performed monthly, while impeller inspection may be performed every 6 months.
- Implement the maintenance plan and monitor its effectiveness: The maintenance plan should be implemented and monitored to ensure that it is effective in preventing failures and improving the reliability of the centrifugal pump.
- By applying RCM maintenance to a centrifugal pump, maintenance tasks can be prioritized and performed based on the risk of failure, leading to improved reliability and reduced maintenance costs over time.
How is RCM maintenance different from other maintenance?
RCM (Reliability Centered Maintenance) maintenance is different from other maintenance strategies because it is a systematic approach to maintenance that focuses on maximizing the reliability of equipment while minimizing the risk of failure.
Here are some key differences between RCM maintenance and other maintenance strategies:
- Reactive Maintenance: Reactive maintenance, also known as “breakdown maintenance,” is performed after a failure occurs. The focus is on fixing the problem quickly and getting the equipment back up and running. RCM, on the other hand, takes a proactive approach to maintenance by identifying potential failure modes and implementing maintenance tasks to prevent failures from occurring.
- Preventive Maintenance: Preventive maintenance, also known as “scheduled maintenance,” involves performing maintenance tasks on a regular basis to prevent failures from occurring. The tasks are usually performed based on the equipment’s operating hours or time intervals. RCM maintenance takes a more targeted approach by identifying the critical components and failure modes of equipment and prioritizing maintenance tasks based on the risk of failure.
- Predictive Maintenance: Predictive maintenance uses advanced tools and techniques to predict when failures are likely to occur. RCM may use predictive maintenance techniques in combination with other maintenance strategies, but the focus is still on identifying and prioritizing maintenance tasks based on the risk of failure.
- Proactive Maintenance: Proactive maintenance is similar to RCM maintenance in that it involves identifying potential problems before they occur. However, proactive maintenance may focus on a broader range of issues, such as improving equipment efficiency, reducing energy consumption, and minimizing environmental impact.
In summary, RCM is a comprehensive and proactive approach to maintenance that is focused on improving equipment reliability and minimizing the risk of failure. It differs from other maintenance strategies in its systematic approach to identifying and prioritizing maintenance tasks based on the risk of failure.
Comparison of RCM maintenance to all other types of maintenance
Reactive Maintenance Vs RCM
Reactive maintenance is performed after a failure occurs, and the focus is on fixing the problem quickly and getting the equipment back up and running. This maintenance strategy is a highly inefficient and expensive method that often leads to unplanned downtime and decreased productivity. In contrast, RCM maintenance takes a proactive approach to maintenance by identifying potential failure modes and implementing maintenance tasks to prevent failures from occurring.
Preventive Maintenance Vs RCM
Preventive maintenance involves performing maintenance tasks on a regular basis to prevent failures from occurring. The tasks are usually performed based on the equipment’s operating hours or time intervals. RCM maintenance takes a more targeted approach by identifying the critical components and failure modes of equipment and prioritizing maintenance tasks based on the risk of failure. Therefore, RCM maintenance provides a more efficient and cost-effective maintenance program than preventive maintenance.
Predictive Maintenance Vs RCM
Predictive maintenance uses advanced tools and techniques to predict when failures are likely to occur. This maintenance strategy is effective in identifying and resolving equipment issues before they occur. However, it requires expensive equipment and specialized personnel to implement, making it less accessible and more expensive than RCM maintenance. RCM may use predictive maintenance techniques in combination with other maintenance strategies, but the focus is still on identifying and prioritizing maintenance tasks based on the risk of failure.
Proactive Maintenance Vs RCM
Proactive maintenance is similar to RCM in that it involves identifying potential problems before they occur. However, proactive maintenance may focus on a broader range of issues, such as improving equipment efficiency, reducing energy consumption, and minimizing environmental impact. RCM is a more targeted approach that focuses on identifying and prioritizing maintenance tasks based on the risk of failure.
In summary, RCM is a comprehensive and proactive approach to maintenance that is focused on improving equipment reliability and minimizing the risk of failure. It differs from other maintenance strategies in its systematic approach to identifying and prioritizing maintenance tasks based on the risk of failure. RCM is a more targeted and cost-effective approach to maintenance than preventive maintenance and reactive maintenance, and it can be more accessible and practical than predictive maintenance.
Skills required in RCM in details
The successful implementation of RCM requires a variety of technical and interpersonal skills. Here are some of the key skills required in RCM :
- Technical Knowledge: RCM requires a strong understanding of the technical aspects of equipment and the maintenance tasks required to keep it running efficiently. This includes knowledge of the various failure modes that can occur, as well as the maintenance strategies and techniques needed to prevent them.
- Data Analysis: RCM relies heavily on data analysis to identify the failure modes that are most likely to occur and to prioritize maintenance tasks based on their impact on equipment reliability. This requires a strong understanding of statistical analysis and data visualization techniques.
- Communication: Effective communication is critical in RCM. This includes the ability to explain complex technical information to non-technical stakeholders, as well as to collaborate effectively with maintenance teams and other stakeholders involved in the maintenance process.
- Problem-Solving: RCM requires a strong problem-solving ability to identify the root causes of equipment failures and to develop effective maintenance strategies to prevent them. This includes the ability to think creatively and to develop innovative solutions to complex problems.
- Project Management: RCM often involves complex projects that require coordination across multiple departments and stakeholders. This requires strong project management skills, including the ability to plan and manage project timelines, budgets, and resources.
- Continuous Learning: The field of maintenance and reliability is constantly evolving, and RCM practitioners need to stay up-to-date with the latest industry trends, technologies, and best practices. This requires a commitment to continuous learning and professional development.
In summary, RCM requires a combination of technical and interpersonal skills, including strong technical knowledge, data analysis, communication, problem-solving, project management, and a commitment to continuous learning.
5 W of RCM maintenance
Reliability Centered Maintenance (RCM) is a proactive maintenance strategy that focuses on improving equipment reliability and minimizing the risk of failure. Here is a detailed description of when, where, how, and why RCM is implemented:
When RCM maintenance
RCM is typically implemented when equipment downtime has a significant impact on production and revenue. It is also commonly used when equipment is critical to safety, such as in the aerospace, nuclear, and healthcare industries. RCM is a proactive approach, so it is implemented before equipment failures occur, usually during the design or installation phase of new equipment or during a major overhaul or upgrade.
Where RCM maintenance
RCM is applicable to any type of equipment, from complex manufacturing equipment to simple systems like HVAC units. It is most commonly used in industries that require high levels of reliability, such as aviation, transportation, energy, and healthcare. RCM can be applied to any equipment regardless of its age, and it can be used to extend the life of aging equipment and improve its reliability.
What RCM maintenance
RCM, or Reliability Centered Maintenance, is a systematic process for analyzing and improving maintenance strategies to maximize equipment reliability and performance.
How RCM maintenance
RCM involves identifying the functions and failure modes of equipment, evaluating the consequences of failure, and selecting the most effective maintenance tasks to mitigate those failures. This includes preventive, corrective, and predictive maintenance tasks, as well as upgrades or modifications to equipment.
Why is RCM maintenance
RCM is important because it helps organizations optimize maintenance costs and reduce downtime, while improving safety and regulatory compliance. By developing effective maintenance strategies, organizations can minimize the risk of equipment failure and maximize equipment reliability and performance.
Why RCM maintenance
RCM is needed because it allows organizations to identify and address potential equipment failures before they occur, preventing downtime and reducing costs associated with unplanned maintenance or equipment failure.
How RCM maintenance
RCM is implemented through a series of steps, including initial data gathering, functional analysis, failure modes and effects analysis, task selection, and implementation. This process is often facilitated by RCM software or other tools to ensure accuracy and consistency.
The RCM maintenance process typically involves seven steps:
- Identify the system or equipment to be analyzed
- Define the system’s functions and performance standards
- Identify the potential failure modes and their consequences
- Determine the causes of the failure modes
- Develop maintenance tasks to prevent or mitigate failures
- Prioritize the maintenance tasks based on their impact on equipment reliability
- Implement and continually evaluate the maintenance program
The RCM maintenance process is typically conducted by a multidisciplinary team that includes maintenance personnel, engineers, operators, and other stakeholders.