- corrective Maintenance
definition of corrective maintenance
Corrective maintenance is an important part of effective maintenance operations that can help to improve the reliability, safety and performance of your equipment. In this guide explain the basics of corrective maintenance including how it differs from preventive maintenance, what types of failure occur, and how you can create a corrective maintenance plan for your plant or organization.
This maintenance is the process of troubleshooting and repairing equipment failures. It’s generally applied after preventive maintenance has failed, during a breakdown or emergency situation. Corrective maintenance seeks to identify and fix the root cause of an issue, preventing the same problem from recurring in the future.
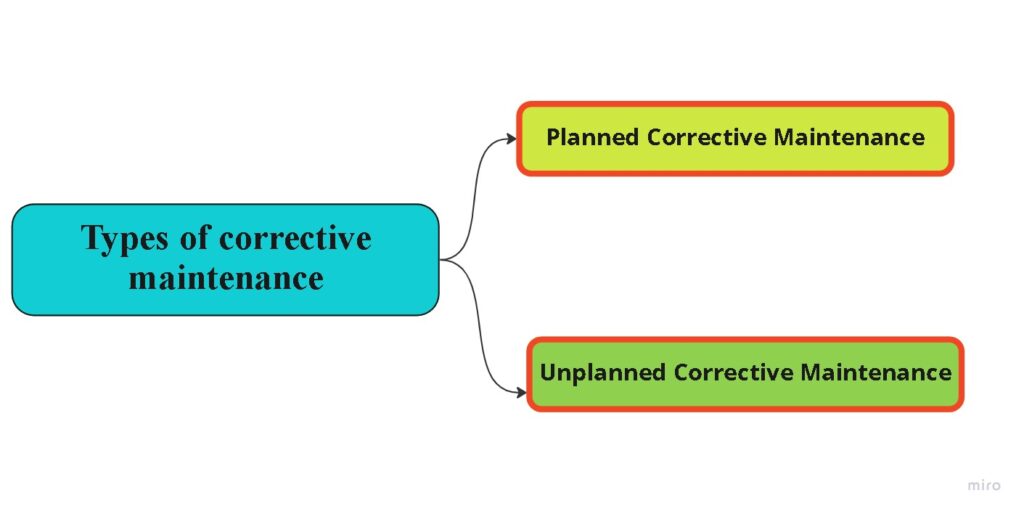
Types of corrective maintenance
Corrective maintenance is an important part of any maintenance program. It includes both planned and unplanned tasks to help keep equipment and machinery in good working order. That also helps to ensure the longevity of machines, as well as improve their overall performance and efficiency. There are two types of corrective maintenance use in industries these are as below.
Planned corrective maintenance
Planned corrective maintenance involves a preplanned strategy for identifying and resolving any malfunction with existing systems or machines that prevent normal operation. This type of maintenance can be planned in either a reactive manner, responding to occurrences as they happen, or through proactive strategies, such as regular inspects and preventive maintenance.
Corrective Maintenance is the process of repairing or replacing a part or system during breakdown. This type of maintenance is typically used in conjunction with run-to-failure maintenance strategies, as assets are allowed to run until they reach a state where repair or replacement may become necessary. This strategy generally works best with non-critical systems and assets, which can be easily and cheaply replaced or repaired, or with systems.
It can either be carried out as part of preventive maintenance to identify and correct issues before they cause equipment failure, or it can also be done through condition-based monitoring. Once the malfunction has been found, corrective maintenance can then be planned and scheduled accordingly.
Unplanned corrective maintenance
Unplanned corrective maintenance is unplanned when it is conducted either out of necessity due to an unexpected failure or in response to a scheduled inspection that reveals a need for repair or replacement. It is performed when an unplanned breakdown occurs outside of the predetermined preventive maintenance schedule. The response time for corrective maintenance will depend on what tools, parts, and personnel are available at that moment. It may also be rescheduled to a later date based on availability of resources.
This is an unplanned maintenance activity wherein an asset undergoes repair or replacement after it has either exhibited signs of potential failure or reached complete breakdown. This type of maintenance does not involve any prior planned activities to detect the damage before it happens or to address the fault after it occurs.
Identifying Problems with Corrective Maintenance
This is most effective when the root cause of an issue can be identified quickly and efficiently. The many diagnostic tools, such as vibration analysis, thermography, and oil analysis help to identify problems quickly before becoming catastrophic failures. But it’s important to work with skilled personnel to analyze the data captured in order to find a reliable solution that will stand the test of time.
Corrective Maintenance Examples
Corrective Maintenance may involve repairing or replacing damaged equipment, correcting errors in a process, troubleshooting and tuning systems, or performing preventive maintenance. It can be applied to many different types of items including machinery and automated systems, networks, software applications, and even workspaces.
- Examples of corrective maintenance might include replacing worn parts on machinery, troubleshooting electrical issues with automated systems and computers, re-configuring networks, updating applications with security fixes or bug fixes and reorganizing workspaces to improve efficiency.
Corrective maintenance is the act of repairing or restoring a machine, component or part that has suffered significant wear. - This type of maintenance often follows preventive maintenance, in which equipment and machines are regularly inspected to detect signs of damage.
- If an issue such as extensive wear is identified during a preventive maintenance inspection, then a corrective action plan should be created within the month to fix the issue.
- Corrective maintenance is performed when an issue arises, or to fix an existing problem.
- An example of this would be a repair technician finding clogged filters on an HVAC system during an emergency repair on a cold winter day. The action then taken would be to clean or replace the filters in order to restore system efficiency and prevent any further loss of heat.
- Corrective maintenance is any maintenance or repair process done to improve the functionality of a system, equipment, or machine. This type of maintenance fixes problems found during routine checks and inspections to restore it to its original condition or specification.
- For example, if a technician notices that signage has been damaged by a storm during a public works project, they can enter an order for corrective maintenance and have it fixed at a later date.
Understanding the Benefits of Corrective Maintenance
- Corrective maintenance is essential in ensuring long-term reliability, but there are several important benefits of corrective maintenance.
- This type of maintenance allows technicians to fix specific issues without having to perform a full overhaul or replacing the entire system.
- It also minimizes downtimes, reduces the overall cost of maintaining equipment and helps ensure that machines or processes are operating in their optimal condition.
- It is also extended asset life, improved efficiency, and lower costs. I attempts to fix a machine before an emergency repair is needed.
- This form of maintenance is usually less costly than emergency repairs, and can help to decrease the amount of emergency orders generated.
- If timely corrective actions are taken, organizations have the potential to reduce costly emergency maintenance jobs.
- Corrective maintenance is an important process in encouraging employee safety.
- This proactive approach to maintenance identifies and flags any issues that can potentially pose a risk, allowing for necessary corrective actions to be taken before serious accidents and incidents occur.
- That can greatly reduce service interruptions by allowing maintenance teams to schedule and prioritize their work orders in a computerized maintenance management system (CMMS).
- This will help them to identify and solve problems as soon as possible, preventing any delays in production or services and keep assets are condition possible with extending their service life.
- Through regular check-ups and identifying issues before they affect other components of a machine, businesses can take corrective action to ensure that vital assets remain in optimal condition.
- Corrective maintenance helps to ensure that resources are used efficiently and it can be much easier for the organization to review, prioritize and schedule jobs for maximum efficiency.
- This allows them to save money and labor in the long run!
- Corrective Maintenance is a type of maintenance procedure which involves addressing existing problems with equipment to reduce downtime.
- It can also help companies to identify any issues that may arise in the future, as early detection of wear and tear can lead to corrective measures being taken before a breakdown or downtime occurs.
- This type of maintenance is important for ensuring that machinery operates efficiently and safely.
Implementing a Structured Schedule for Corrective Maintenance
A structured schedule for corrective maintenance must be implemented in order to ensure that any problems are identified and addressed as soon as possible. This requires regularly performing inspections and having a system in place for recording and storing data on machine performance over time.
When reporting maintenance issues, technicians should also describe the nature of the problem as accurately as possible, including details about replacement parts that may need to be ordered. By following these steps, you’ll be able to identify and effectively fix any potential issues with your equipment quickly and efficiently.
How can improve corrective maintenance
The end User education and training can greatly improve the performance of maintenance operations. By teaching your personnel how to use and maintain equipment correctly, you can reduce the number of corrective maintenance incidents that occur. It is also important to create procedures for reporting any irregularities, in addition to providing guidance about steps to be taken if a machine needs to be serviced or repaired. Additionally, making sure that your team is regularly trained on the principles of preventive maintenance will ensure that all machinery operates safely, accurately, and reliably.
When should you use corrective maintenance?
It is a type of maintenance that is only necessary in certain cases, and should not be depended on for day-to-day operations. The 80/20 rule applies here – it’s important to prioritize preventive maintenance by devoting 80 percent of resources towards it, while focusing 20 percent of attention on corrective maintenance. Factors such as asset criticality, downtime costs, and swappable parts are factors to consider when deciding how much reliance to place on corrective maintenance.
Corrective Maintenance is the process of using a specialized computer management software (CMMS) to organize, optimize and customize your maintenance strategy. By collecting and storing detailed information on your assets, it becomes much easier to make well-informed decisions that will help manage costs effectively.
Maximizing Corrective Maintenance
Corrective maintenance is a critical part of any organization’s routine maintenance plan. Technicians are trained to identify, diagnose and repair potential issues quickly and efficiently before that create major problems.
To ensure effective corrective maintenance, companies should invest in the training and education of their maintenance staff. Equipping them with the knowledge to identify potential issues while carrying out preventive or emergency maintenance services will help mitigate further costly repairs.
Corrective Maintenance, however, is an important part of any facility’s maintenance strategy as it aims to fix existing issues as soon as possible. To help with this, organizations should create regular maintenance checklists that technicians can use to identify potential problems quickly in order to generate corrective maintenance orders and keep the facility running optimally.
How Corrective Maintenance Improves Reliability
When it comes to Corrective Maintenance, the goal is to restore a piece of equipment to its peak performance. However, corrective maintenance provides an additional benefit in that it can also be used to quickly inspect the item and identify any underlying issues that could affect reliability.
By taking advantage of this opportunity, corrective maintenance can be used to help ensure peak operation for the equipment. That is repairs or replaces parts that are broken. When a corrective maintenance order is triggered by a failure mode, it is essential to check the possible cause and origin of the failure in the first place. Through such action, the likelihood of similar or repeated occurrences of failure can be lowered and asset reliability strengthened.
An example would be repacking a process pump, which is necessary when the packing fails. When this takes place, technicians should make a checklist of simple inspections too; like checking the wear and tear on the throat bushing, inspecting the shaft run-out, and looking at the water pressure.
This will ensure that any future corrective maintenance needs are identified. It includes the diagnosis and resolution of any problems, faults, or defects that have occurred, as well as the inspection of equipment to ensure that it is operating correctly and safely. By incorporating these inspections into the CM process, businesses can improve their plant reliability and optimize their operations.
Advantages of Corrective Maintenance
- Corrective Maintenance refers to the process of fixing a known issue or problem.
- It requires having knowledge of the product, troubleshooting, and on-site repair.
- This type of maintenance has advantages such as efficient repair time, improved system health and decreased downtime.
- For businesses that encounter unexpected failures in the course of their operations, corrective maintenance is an important way to address and repair them.
- This type of maintenance strategy involves identifying issues, repairing the problem, and returning the system to a fully operational state.
- Corrective maintenance helps organizations remain as efficient and productive as possible by addressing any vulnerabilities quickly.
- It is essential when implementing corrective maintenance in order to optimise production and efficiency.
Disadvantages of Corrective Maintenance
- It can also be costly and often require additional parts or even system adjustment.
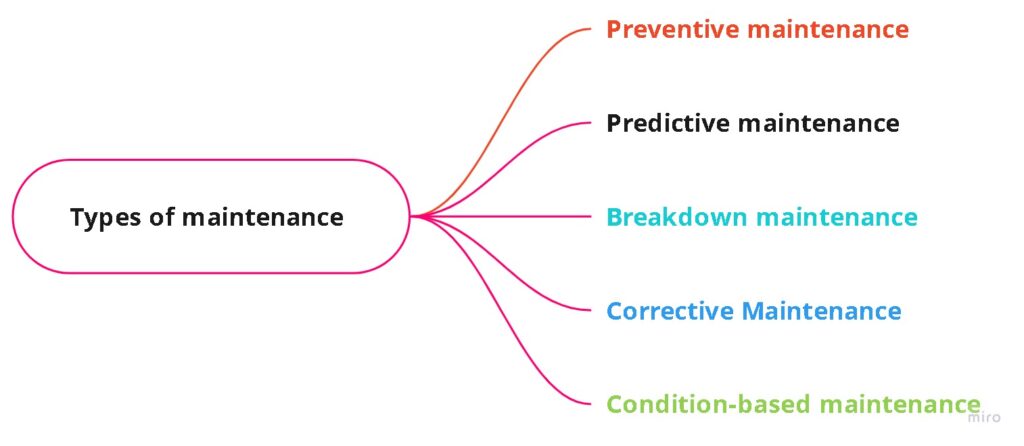
- It differs from preventive and predictive maintenance programs, which attempt to anticipate problems before they arise or lead to failure.
Corrective vs. Breakdown Maintenance
Corrective Maintenance is a type of equipment maintenance aimed at fixing or optimizing an appliance or piece of machinery that has become faulty or broken.
Breakdown maintenance, which generally focuses on rapidly responding to an emergency situation and restoring normal operations as soon as possible.
Corrective maintenance is a type of maintenance that focuses on fixing and repairing broken or faulty equipment.
It is different from breakdown maintenance, which is when equipment that has stopped working is repaired to get it back up and running again.
Corrective maintenance refers to the repair and replacement of components or equipment after something breaks in order to restore it to its original condition.
This type of maintenance is typically performed in response to a failure, meaning that there was a lack of preventive maintenance which resulted in the need for repairs.
What is the difference between preventive and corrective maintenance?
preventive maintenance vs corrective maintenance
Preventive maintenance takes a proactive approach to facility maintenance and is usually conducted on a planned schedule.
Checking lubrication is an important task in this preventive process.
Corrective Maintenance (CM) is the act of repairing or replacing parts of equipment that is suddenly malfunctioning due to a breakdown of some sort. It is carried out without any prior warning as opposed to preventive maintenance.
The corrective maintenance involves activities that are regularly scheduled in order to reduce wear and tear, increase life expectancy and minimize failure.
CM is usually used as a means for restoring an item to its optimal working condition after it has broken down.
CM is a type of maintenance which is carried out after a mechanical or electrical system has stopped working.
It involves locating the fault and repairing it in order to restore the system’s functionality.
This type of maintenance usually requires detailed troubleshooting and diagnostic procedures to fix faults quickly and accurately.
Corrective Maintenance is the process of regularly inspecting equipment and facilities in order to identify any possible problems, and then taking action in order to prevent or fix any such issues.
The motive of maintenance is ensuring the equipment remains safe and reliable with regular, routine inspections that can help detect potential problems before they become serious issues.
Corrective maintenance, also known as break-fix maintenance, refers to maintenance that is done in response to a breakdown or malfunction.
Examples of corrective maintenance include changing filters, fixing broken parts, troubleshooting electrical components, and replacing worn out parts, checking vents (clogged or blocked) etc.
It is important to regularly carry out corrective measures such as these in order to ensure optimal efficiency of the ventilation system.
Companies use special maintenance-tracking software to help them manage corrective maintenance efficiently and in a timely manner. This type of software helps keep systems and assets up and running, allowing companies to be more productive with their time and resources.
Corrective Maintenance, also known as proactive maintenance, is a type of maintenance used to prevent or fix breakdowns on assets and equipment. Utilizing an effective CMMS (computerized maintenance management system) can dramatically reduce the amount of time required to address corrective issues, improve asset reliability and extend equipment life-cycle.
With a comprehensive CMMS, you can quickly prioritize maintenance requests and store critical data such as warranties and asset tags in one centralized location.
A great CMMS can help you streamline your workflow and provide better insights into how your facility is running.
How Does a CMMS Help With Corrective Maintenance?
Corrective Maintenance is a process used in Computerized Maintenance Management Systems (CMMS) to identify, track, and address issues with equipment or assets as they arise. This involves providing timely repairs and preventive maintenance services to ensure assets remain operational and accurate records of maintenance activities can be documented.
Corrective Maintenance is a type of maintenance designed to fix errors or malfunctions in a system or device. It involves identifying the problem and making adjustments, repairs, or replacements to restore the system or device to working order. CM also includes scheduled maintenance activities that prevent problems from arising in the first place. CM is the act of identifying, repairing and/or replacing defective equipment or parts with the goal of restoring them to their optimal working condition.
It involves manually eliminating data entry errors as well as enabling mobility by providing resources such as mobile computers and electronic forms to personnel in the field. It involves diagnosing and solving the issue as quickly as possible, as well as recording historical data and statistics of the equipment in order to prevent any future issues. CM is the process of repairing or replacing faulty equipment or parts in order to maintain optimal operation and performance.
This includes tracking equipment health, labor, inventory, costs, and work orders to ensure that maintenance is completed efficiently and correctly. It is an extremely helpful software that helps businesses identify operating problem spots quickly and accurately and schedule technicians for fixes as soon as possible. This technology helps reduce downtime, promotes more efficient repairs and maximizes productivity.
Corrective maintenance is an important tool for tracking the maintenance histories of your assets, as it allows you to make more informed decisions when it comes to replacement and repair. It gives you insight into whether a particular machine is costing you more money than it is worth, making it easy to decide when it’s time to upgrade and make the switch to a more reliable model. CMMS (Computerized Maintenance Management System) software can be used to effectively track required inventory for carrying out corrective maintenance tasks, helping you ensure that the correct parts are always on-hand and preventing any last minute orders.
Corrective maintenance is a type of maintenance that helps improve operational efficiency by focusing on the repair and replacement of parts. This type of maintenance saves both time and money, as it reduces waste and increases productivity. It can also help to improve safety measures when used correctly, ensuring that machine problems are spotted and rectified quickly before they cause larger issues.
Conclusion
Corrective maintenance is a type of maintenance activity designed to address operational issues and restore malfunctioning equipment back to its designed state. This type of maintenance is important as it helps to ensure that equipment and machinery runs at optimal levels. However, it is also important to understand the potential costs associated with corrective maintenance in terms of efficiency and downtime, in order to avoid any potential losses in productivity. Corrective maintenance is a key part of any maintenance team’s toolbox. It involves quickly identifying and fixing issues that arise in the course of operating machinery, as opposed to preventive or predictive maintenance which seeks to stop them from occurring in the first place. By using data analysis to determine when and where corrective maintenance should be employed, maintenance teams can ensure their efforts are best used to maximize machine efficiency.