Pipe Fittings
Pipe fittings are used to connect pieces of pipe together, as well as provide strength and stability to piping systems. Depending on the type of fitting, they can be used to control flow, change direction, or even assist with insulation and noise reduction by providing a seal at connections.
Pipeline fittings are an essential part of any pipeline system. These fittings help connect different parts of the pipeline, allowing for the efficient flow of fluids or gases. Some of the most common fittings include various types of valves, couplings, elbows, tees, reducers, and flange.
Importance of Pipeline fittings:
- Pipeline fittings play a role in ensuring the safety and integrity of the pipeline system.
- These fittings help to regulate the flow of fluids or gases in pipeline.
- Pipeline fittings help to prevent any leakage or failure in the pipeline.
- They facilitate maintenance and repair work on the pipeline system.
Standards for Pipeline Fittings:
There are various standards that define the design and manufacturing requirements of pipeline fittings. These standards include:
- AS B16.9: This standard specifies the dimensions of factory-made wrought steel and alloy steel-welding fittings.
- MSS SP-75: This standard covers high-strength, alloy steel butt-welding pipe fittings.
- ASME B16.11: This covers forged steel fittings.
- ANSI B16.5: This standard specifies the dimensions of pipe flanges and flanged fittings.
FOLLOW THE LINK TO DOWNLOAD PDF FREE BY FOLLOW – LINK
Types of pipe fittings
Pipe fittings are used to connect and join different sections of pipes thereby making it possible for fluids or gases to flow smoothly. There are various types of pipe fittings available in the market each serving a particular function. Some of the most commonly used types of pipe fittings include:
|
Elbow
An elbow is a pipe fitting that is used to change the direction of the pipeline. It is available in different angles such as 45°, 90°, and 180°. Elbows are typically made from materials such as carbon steel, stainless steel, and cast iron.
Types of elbow:
There are two main types of elbows –
- Long radius elbows
- Short radius elbows.
Long radius elbows have a larger radius and are used in low-pressure applications, while short radius elbows have a smaller radius and are used in high-pressure applications.
Codes and specifications of pipe elbow:
Pipe elbows are fittings that are used to change the direction of the flow of fluids in piping systems. The following are some of the codes and specifications for pipe elbows:
- ANSI/ASME B16.9: This code specifies the dimensions of wrought steel and wrought iron butt-welding fittings, including pipe elbows. It covers the design, materials, manufacturing, testing, and inspection of these fittings.
- ASTM A234: This specification covers wrought carbon steel and alloy steel fittings of seamless and welded construction. It includes pipe elbows, among other types of fittings, and covers their dimensions, materials, and mechanical properties.
- MSS SP-75: This specification covers high-strength, low-alloy steel fittings, including pipe elbows, for use in pipelines. It covers their design, materials, manufacture, testing, inspection, marking, and packaging.
- ASME B16.28: This code covers the dimensions and tolerances for short-radius and long-radius pipe elbows made of wrought carbon steel and alloy steel.
- DIN 2605: This specification covers the dimensions and tolerances for seamless and welded steel pipe elbows. It includes both short-radius and long-radius elbows and covers their materials and pressure ratings.
- ISO 3419: This standard specifies the design, dimensions, and pressure ratings of steel pipe elbows for use in pipelines. It includes both long-radius and short-radius elbows and covers their manufacturing, testing, and inspection.
Tee:
A tee is a pipe fitting that is used to join three pipes together at right angles. Tees are typically made from materials such as carbon steel, stainless steel, and cast iron.
Types:
There are several types of teas, including
- Straight tees,
- Reducing tees
- Barred tees
Straight tees have equal-sized outlets, reducing tees have different-sized outlets, and barred tees have a branch that is partially closed off.
Codes and Specifications:
Pipe tees are fittings that are used to join three pipes or tubes at right angles to one another. The following are some of the codes and specifications for pipe tees:
- ANSI/ASME B16.9
- ASTM A234
- MSS SP-75
- ASME B16.28
- DIN 2615
- ISO 3419
Reducer:
A reducer is a pipe fitting that is used to connect pipes of different sizes. It is typically made from materials such as carbon steel, stainless steel, and cast iron.
Types:
There are two main types of reducers –
- Concentric reducers
- Eccentric reducers
Concentric reducers have an asymmetrical shape and are used to connect pipes of different sizes with a common centerline, while eccentric reducers have an asymmetrical shape and are used to connect pipes of different sizes that are not on a common centerline.
Codes and Specifications of pipe reducer:
Pipe reducers are fittings that are used to connect two pipes of different sizes. The following are some of the codes and specifications for pipe reducers:
ANSI/ASME B16.9, ASTM A234, MSS SP-75, ASME B16.11, DIN 2616, ISO 15590 etc.
Coupling:
A coupling is a pipe fitting that is used to connect two pipes together. It is typically made from materials such as carbon steel, stainless steel, and cast iron.
Types of pipe coupling
There are several types of pipe coupling used in various industries, and some of the most common types include:
- Threaded Coupling: This type of coupling is used to join two pipes that have male threads on the outside. It consists of two halves that are screwed together.
- Compression Coupling: This type of coupling is used to join pipes of the same diameter. It consists of a sleeve that is compressed onto the pipe using a compression nut.
- Flanged Coupling: This type of coupling is used to join pipes that have flanges on the ends. It consists of two flanges that are bolted together with a gasket in between.
- Welded Coupling: This type of coupling is used to join two pipes permanently by welding them together.
- Grooved Coupling: This type of coupling is used to join pipes that have been grooved on the ends. It consists of two halves that are bolted together around the grooves.
- Quick Coupling: This type of coupling is used to connect and disconnect pipes quickly and easily. It consists of two halves that are pushed together and locked in place.
Codes and specifications of pipe coupling
Pipe couplings are fittings that are used to connect two pipes together. The following are some of the codes and specifications for pipe couplings:
- ANSI/ASME B16.11: This code covers the dimensions and tolerances for forged fittings, including pipe couplings, made of wrought carbon steel and alloy steel.
- ASTM A105/A105M: This specification covers carbon steel forgings for piping applications, including pipe couplings. It covers their chemical composition, mechanical properties, and testing requirements.
- ASTM A234/A234M: This specification covers wrought carbon steel and alloy steel fittings of seamless and welded construction. It includes pipe couplings, among other types of fittings, and covers their dimensions, materials, and mechanical properties.
- MSS SP-83: This specification covers Class 3000 and 6000 threaded pipe couplings, including full couplings and half couplings. It covers their dimensions, materials, and marking requirements.
- ISO 8434-1: This standard specifies the dimensions and performance requirements for hydraulic fluid power quick-action couplings used in industrial and mobile equipment. It includes pipe couplings and covers their materials, dimensions, and testing requirements.
- API 5L: This specification covers seamless and welded steel line pipe, including pipe couplings, for use in conveying gas, water, and oil in the petroleum and natural gas industries. It covers their chemical composition, mechanical properties, and testing requirements.
Union:
A union is a pipe fitting that is used to connect two pipes together in a way that allows for easy disassembly. It is typically made from materials such as carbon steel, stainless steel, and brass.
Types of pipe union:
There are several types of unions, including
- Threaded unions
- Flanged unions
- Compression unions
Threaded unions are screwed onto the pipe ends, flanged unions are bolted onto the pipe ends, and compression unions are tightened onto the pipe ends using a compression nut.
Codes and Specifications of pipe union:
Pipe unions are fittings that are used to join two pipes together, allowing for easy disassembly and reassembly of the connection. The following are some of the codes and standards for pipe unions:
- ASME B16.39:
- ASME B16.11
- ASTM A182/A182M
- MSS SP-83
- API 5L
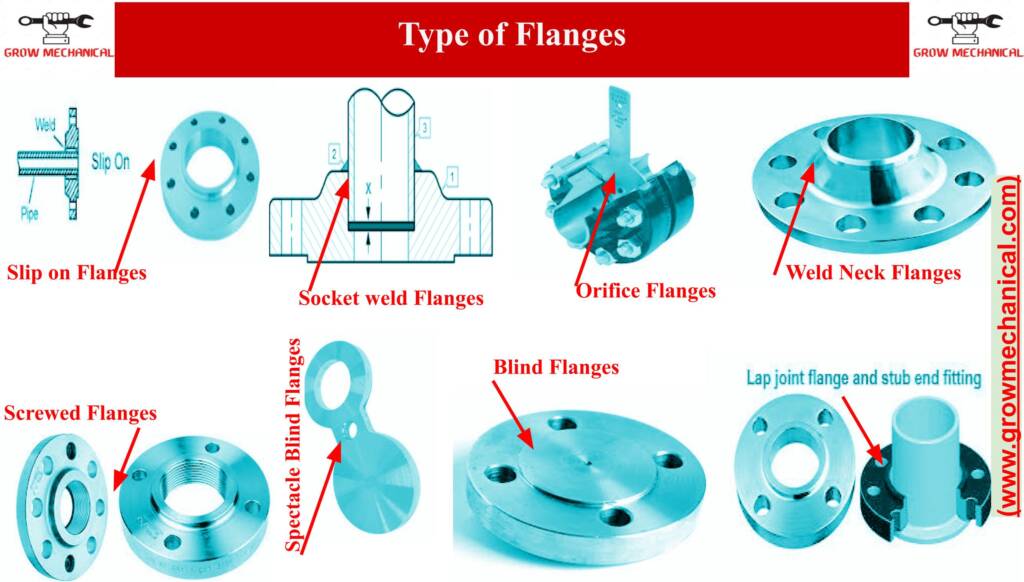
Flange:
A flange is a plate or ring that is used to connect two pipes together by bolting them together. It is typically made from materials such as carbon steel, stainless steel, and cast iron.
Types of pipe Flange:
There are several types of flanges, including slip-on flanges, weld-neck flanges, and blind flanges. Slip-on flanges are slid onto the pipe ends and welded in place, weld-neck flanges are welded onto the pipe ends, and blind flanges are used to seal off the end of a pipe.
Codes and Specifications of pipe Flange:
Pipe flanges are fittings that are used to connect pipes, valves, pumps, and other equipment to form a piping system. The following are some of the codes and standards for pipe flanges:
- ASME B16.5: This code covers the dimensions, tolerances, materials, and marking requirements for steel pipe flanges and flanged fittings from NPS 1/2 to NPS 24. It includes weld neck, slip-on, threaded, lap joint, socket weld, and blind flanges.
- ASTM A105/A105M
- ASTM A182/A182M
- MSS SP-44
- API 6A.
- ISO 7005-1: This standard specifies the flange dimensions for steel pipe flanges from DN 10 to DN 4000. It includes weld neck, slip-on, threaded, lap joint, socket weld, and blind flanges.
Nipple:
A nipple is a short piece of pipe that is used to connect two fittings together. It is typically made from materials such as carbon steel, stainless steel, and brass.
Types of Nipple:
There are several types of nipples, including
- Threaded nipples
- Close nipples
- Hex nipples.
Threaded nipples are screwed into fittings, close nipples are used to extend the length of a fitting, and hex nipples have a hexagonal shape for easy tightening.
Codes and Specifications of Nipple:
Pipe nipples are short pieces of pipe with male threads at both ends used to connect two female threaded pipes together. The following are some of the codes and standards for pipe nipples:
- ASME B16.11
- ASTM A733
- MSS SP-95
- API 5L
Pipe cap
Pipe caps can be used for a variety of reasons, including to prevent contamination of fluids or gases within the pipe, to prevent dirt and debris from entering the pipe, or to protect the end of the pipe from damage. They can be used in a wide range of applications across many industries, including oil and gas, chemical processing, and water treatment. Here are some common types of caps, as well as codes and standards that apply to them:
Types of pipe cap
- End Cap – A type of cap that is used to close the end of a pipe.
- Blind Cap – A type of cap that is used to close the end of a pipe but has no opening.
- Threaded Cap – A type of cap that has female threads and is screwed onto the end of a male pipe.
- Welded Cap – A type of cap that is welded onto the end of a pipe.
Here are some common codes and standards that apply to pipe caps:
- ASME B16.9 – Factory-Made Wrought Steel Buttwelding Fittings. This standard covers the dimensions and tolerances for butt-welded pipe caps made from materials such as carbon steel, stainless steel, and alloy steel.
- ASME B16.11 – Forged Steel Fittings, Socket-Welding and Threaded. This standard covers the requirements for forged pipe caps (socket-weld and threaded) made from materials such as carbon steel, alloy steel, stainless steel, and nickel alloys.
- MSS SP-43 – Wrought Stainless Steel Butt-Welding Fittings. This standard covers the dimensions, tolerances, and markings for stainless steel butt-welded pipe caps.
- ASTM A234 – Piping Fittings of Wrought Carbon Steel and Alloy Steel for Moderate and High Temperature Service. This specification covers wrought carbon steel and alloy steel pipe caps for use in moderate and high-temperature service.
- ANSI/ASME B1.20.1 – Pipe Threads, General Purpose (Inch). This standard covers the general-purpose pipe threads used for threaded pipe caps in the United States.
Union:
A union is a type of fitting that connects two pipes, for easy disassembly and reassembly. It consists of three parts: a nut, a female, and a male end. The female and male ends are threaded on the inside and outside respectively, and the nut is used to join them together. Unions are typically used in where regular maintenance or repair is necessary.
Codes and specifications of Union
Here are some of the codes and standards for pipe unions:
- ASME B16.39: Covers the dimensions, design, materials, and marking requirements for threaded pipe unions made of malleable iron or brass.
- ASME B16.11:
- ASTM A105/A105M, ASTM A182/A182M
- MSS SP-83: Covers Class 3000 and 6000 threaded pipe unions, including full unions and half unions. It covers their dimensions, materials, and marking requirements.
- API 5L
Plug:
A plug is a type of fitting that is used to the end of a pipe. It is similar to a cap, but has a male thread the outside, allowing it to be screwed into a female fitting. Plugs are typically used for where temporary closure is necessary.
Types of Pipe Plugs:
- Threaded Plugs: Have male threads that screw into the female threads of a pipe or fitting.
- Mechanical Plugs: Have a compression nut that expands a rubber or plastic seal to create a tight fit inside the pipe.
- Inflatable Plugs: Have a rubber bladder that is inflated with air or water to seal the pipe.
- Welding Plugs: Are welded onto the end of a pipe to seal it.
Codes and Standards for Pipe Plugs:
- ASME B16.11
- ASTM A105/A105M, ASTM F104
- ISO 9001:2015: Specifies the requirements for quality management systems, including product design, development, and manufacturing, to ensure consistent quality of pipe plugs.
Bushing:
A bushing is a type of fitting that is used to join two pipes or fittings together of different sizes. is typically made from the same material as the pipe or fitting it is joining. Bushings can be threaded or welded to the pipe or fitting.
Pipe bushings are used to connect two pipes of different sizes. The following are the types, codes and standard names, and selection criteria for pipe bushings:
Types of Pipe Bushings:
- Threaded Bushings: Have male and female threads to connect two pipes with different sizes.
- Socket Weld Bushings: Have a socket to fit over the end of a pipe and a smaller diameter socket to fit inside another pipe.
- Butt Weld Bushings: Are welded onto the end of a pipe to reduce its diameter and connect it to another pipe.
Codes and Standard Names for Pipe Bushings:
- ASME B16.11, ASME B16.9
- ASTM A105/A105M, ASTM A182/A182M
Cross
Cross is a pipe fitting that is used to connect four pipes together at right angles. It has four outlets, with one inlet and three outlets or vice versa. Crosses are typically made from materials such as carbon steel, stainless steel, and cast iron.
Types of Cross:
There are several types of crosses, including equal crosses and reducing crosses. Equal crosses have outlets of the same size, while reducing crosses have outlets of different sizes.
Codes and Specifications of Cross:
A cross is a type of pipe fitting that allows four pipes to be connected at right angles to each other. The following are the codes and standards for crosses:
- ASME B16.9
- MSS SP-75
- ISO 15590-2
Lap Joint :
A lap joint is a type of resistance welding that joins two overlapping pieces of metal together. It is a relatively simple joining technique that is used in the manufacturing industry for applications such as sheet metalwork, automotive body panels, and piping.
In a lap joint, the two pieces of metal are overlapped and then clamped together. An electric current is then passed through the joint, which melts the metal at the point contact. After the joint cools, the two pieces of metal are fused together and a seam is formed.
Types of Lap Joint:
-
Single Lap Joint: In this joint the two pieces of metal overlap so that the thickness of the joint is equal to that of the thickest metal piece.
-
Double Lap Joint: In this joint, each piece overlaps by half of its thickness. The joint thickness will be equal to the total thickness of the two of metals.
-
Offset Lap Joint: In this joint, the two pieces metal each other at an angle, creating an offset joint.
Codes and standards for Lap Joint:
The Lap Joint is a type of pipe joint where the end of one pipe overlaps the end of another pipe. Here are some codes and standards that apply to Lap Joint:
- ASME B16.5 – This standard covers pipe flanges and flanged fittings, including lap joint flanges, with dimensions from NPS 1/2 through NPS 24.
- MSS SP-43 – This standard covers Wrought Stainless Steel Butt-Welding Fittings, including lap joint stub ends.
- ASTM A105, ASTM A182
- ANSI/ASME B31.1 – This code covers the design, construction, operation, and maintenance of power piping systems, which includes lap joint flanges.
- ANSI/ASME B31.3 – This code covers the design, construction, operation, and maintenance of process piping systems, which includes lap joint flanges.
Swage nipple
A swage nipple is a pipe fitting that is used to connect two sizes of pipes together. They are typically used in high-pressure piping systems where a reduction in size is required.
Types of swage Nipples:
There are two main types of swage nipples: concentric and eccentric Concentric swage nipples have a uniform diameter throughout the fitting, while eccentric swage nipples have a larger end and a smaller end.
Concentric Swage Nipple:
A concentric swage nipple is a pipe fitting used to reduce the size of a larger pipe to a smaller of the same diameter. This type of swage nipple is typically used in applications where the flow needs to be maintained or increased Eccentric Swage Nipple:
An eccentric sw nipple is a pipe fitting used to connect two pipes of different sizes with one end larger than the. This type of swage nipple is typically used in applications where the flow rate needs to reduced or where there is a need for a change in direction.
Codes and Specifications Swage nipple:
Sw nipples are manufactured to various standards such as ASME B16.11 for forged fittings and AS B16.9 for wrought fittings. The materials used for swage nipples are typically carbon, stainless steel, and alloy steel.
Pipe olets
Pipe olets are a type of fitting that are used to connect piping systems to various equipment and pipelines. They are customarily made of stainless steel or other alloys that are known their durability and resistance to corrosion. Pipe olets come in different shapes, sizes, and configurations and they are engineered to handle various flow rates and pressure ranges, depending on their intended applicationsTypes of Pipe Olets
Pipe olets types
Pipe olets can be classified into several types, depending on their and functions. The most common types of pipe olets include:
-
Weldolet This type of pipe olet is the most commonly used, and it is designed to be directly to the run pipe. Weldolets are often used for high-pressure applications and piping systems carry hazardous materials.
-
Socket Weldolet: A socket weldolet is to be fitted onto the run pipe with a socket weld. They are ideal for use in millimeter piping systems, such as those used in chemical plants, refineries, and petro facilities.
-
Threadolet: Threadolets are threaded pipe fittings that attach to run pipe. They are ideal for low-pressure applications and are often used in fire sprinkler, HVAC systems, and other industrial applications.
-
Sockolet: Socklets are similar to a weldolet, but are designed to be installed using a socket. They are commonly used in small-diameter and low-pressure applications.
Codes and SpecificationsPipe olets are designed to comply with various industry codes and specifications, depending on their intended applications. Some of the most common codes and specifications include:
- ASME B31.1 Piping Code
- ASME B31.3 Process Piping Code
- ASTM A105/A105M-18 Specification for Carbon Steel Forgings for Piping ApplicationsSelection
Stub end Introduction
A stub end is a type of fitting primarily used in piping systems where pipes need to be connected but the final length of the joint cannot be easily predicted. This is achieved by combining a stub end with a lap joint flange. The stub end fits inside, and the two pipes are welded together to create a joint that can be adjusted or without the need for cutting or altering the entire assembly. Stub ends are commonly utilized in piping systems high-pressure, high-temperature, or highly corrosive applications.
Types stub end:
There are two types of stub ends: long pattern and short pattern. Long pattern stub ends have a length that is equivalent to the ASA flange from which it is made, whereas the short pattern stub ends are just a few millimeters long. These two types of stub ends have some differences in terms of their applications, design, and suitability for different pressure ratings.
Codes and Specifications stub end:
Several codes specify the manufacturing, dimensions, and testing requirements for stub ends. These standards include ASME16.9, MSS SP-43, and MSS SP-75 codes. The dimensions range from ½ inch to 24 inches in diameter, and the wall thickness varies from Schedule to Schedule 160, depending on the application.
Pipe saddle Introduction:
A pipe saddle is a type of fitting that is used to connect a or tube to a flat surface. It is a device that provides a secure, stable connection between the pipe and the supporting structure. There are different types of pipe saddles, each designed for applications. They come in different materials, sizes, and shapes, and each type has its unique set of specifications and.
Types of Pipe saddle:
-
Weld-on saddle: type of saddle is welded to the pipe or tube and provides a secure and permanent connection. is typically used in applications where high strength, durability, and stability are required.
-
Thread saddle: This type saddle is used for pipes and tubes that are threaded. It provides a secure and stable connection without the need for welding.
-
Clamp on saddle: This type saddle is used when there is a need to connect pipes or tubes to flat surfaces such as walls and ceilings. It provides a secure and stable connection without the need for welding or threading.
Codes specifications Pipe saddle:
Pipe saddles are subject to certain codes and specifications that ensure their performance and safety These codes include ASME (American Society of Mechanical Engineers) standards, ASTM (American Society for and Materials) standards, and API (American Petroleum Institute) standards. The specifications for pipeles include material type, size, and shape, as well as load capacity and ratings.
Pipe ferrule Introduction:
A pipe ferrule, also known as a compression fitting, is a that connects two pipes or tubes together. The ferrule is designed to provide a secure connection to the need for welding or threading. It is widely used in various industries like oil and gas,, pharmaceutical, etc.
Types of Pipe Ferrules:
There are several types of pipe ferrules, and they can be made of different materials to suit different applications. Some of the most common types are:
- Brass Ferrules: Brass ferrules are commonly used in applications because of their excellent resistance to corrosion and rust.
- Stainless Steel Ferrules: steel ferrules are ideal for high-pressure applications or for use in corrosive environments.
- Plastic Ferrules: Plastic ferrules are light in weight and can be used in instances where metalules are not suitable.
- Carbon Steel Ferrules: Carbon steel ferrules are strong durable, making them ideal use in heavy-duty applications.
Codes and Specifications of Pipe ferrule:
Pipe ferrules manufactured in accordance with various industry standards and specifications. These standards ensure that the ferrules meet requirements for strength, durability, and safety. Some of the most commonly used standards for pipeules are:
- ANSI/ASME B16.5 – Pipe Flanges and Fl Fittings
- ANSI/ASME B16.11 – Forged Fittings, Welding and Threaded
- ASME B31.3 – Process Piping4. ASTM A105105M – Standard Specification for Carbon Steel Forgings for Piping.
Pipe bend definition
Pipe bend is a piping component used for changing the of a piping system. It is suitable for various applications such as petrochemical, oil gas, power generation, and many more industries. It is used to avert pipeline obstruction, fluid friction, and increase the flow rate of fluids.
Types of Pipe Bend:
There are types of pipe bends, including:
- Long Radius Bend: It has a larger radius than other bends. It offers lower fluid resistance but requires more space.
- Short Radius: It has a smaller radius of curvature than a long radius bend. It provides a more compact.
- 3D and 5D Bend: These refer to the radius to relation. A 3D bend is thrice the diameter of the pipe, while a D bend is five times the pipe diameter.
- Mitered bend: This type bend involves cutting and welding two or more pipes to make an angle.
Codes and specifications Pipe ferrule:
Pipe must meet the industry standards, including ASTM A234, ASTM A403, ASME SA, ASME SA403, and ANSI B16.9, which outline the material specifications and tolerances for manufacturing pipe bends. Pressure ratings and temperature limitations must also comply with required standards.
Introduction to Pipe Adapter
A pipe adapter is a fitting that is used to connect pipes or fittings of different sizes or types. Ad can also be used to extend the pipe length, change the end type, or connect pipes with different end types. Pipe adapters are essential components in plumbing and pipeline systems with the capability to join pipes and fittings of different sizes thereby eliminating the need to replace the entire pipe system. The adapter fitting comprises two connecting ends, one standardized and the other of a different diameter or a connection type.
Types of Pipe Adapter
Pipe adapters are available in various types based on the connection type and their function. following are the types of Pipe Adapters:
- Threaded Adapter – This type of connects pipes by screwing designated ends, connected to the pipe of a different size or connection. These adapters are compatible with same-threaded pipes or threads with different standards, such as BSP.
- Slip-on Adapter – This type of adapter allows pipes to slide into them a secure fit. They are compatible with PVC, CPVC, or other plastic or metal.
- Compression Adapter – Compression adapters create a seal by compressing a rubber gasket between metal or plastic fittings. They are commonly used to connect copper or PVC pipes.
- 4.bed Adapter – Barbed adapters have ridges that allow for a secure grip on plastic pipes. clamps are necessary for tight sealing to ensure no leakage.
- Flanged Adapter -Flanged adapters connect pipes with a flat flange end type. Gaskets or O-rings seal the flange adapters.
Codes and Specifications of Pipe Adapters
Here are some common codes and specifications of pipe adapters: ASME B16.11, ASTM A105, ASTM A182, ASTM A234, MSS SP-95, ANSI/ASME B1.20.1 etc.
Introduction pipe strainer:
A pipe strainer is a device placed in a pipeline to remove unwanted particles debris from liquids, gases or steam flowing through it. It protects equipment, such as pumps valves, from damage caused particles that could clog or damage their working parts. Pipe str come in multiple types and sizes, and their specifications selection depends on the intended applications and conditions.
Types of Pipe Strainers:
- Y-Type Strainers – Y strainers are named so because of the Y-shaped body that they possess. They are most commonly used in-flow or minimal volume applications.
- Basket Strainers – Basket strainers are designed to filter out larger particles. They have a cylindrical or conical shape, and they can be made from variety of materials.
- T-Type Strainers – T-type strainers are shaped like a T, and they are designed to filter out smaller particles. They are often used in high-flow.
- Duplex Strainers – Duplex strainers consist of two separate strainers operate in parallel, allowing one strainer to be cleaned while the other is in operation.
Codes and standards of strainers
Here are some common codes and standards that apply to pipe strainers: ASME B16.34, MSS SP-80, API 598, ANSI/ASME B31.1 ANSI/ASME B31.3, AWWA C701, AWWA C508 etc.
Introduction sight glass:
A sight glass is a transparent tube or pane used in the industrial and fields to observe the flow of liquids or gases. The sight glass provides a method to quickly determine the flow rate of fluid, the color of the fluid, and the clarity of the fluid in a pipe or container. This is important because it allows technicians to observe any potential issues or changes to the system, such as leaks or blockages.
Types of sight glass
There are types of sight glasses available, including:
- Tubular sight glasses – these are simple, tubes made of tempered glass, plastic, or metal. They are typically used in low-pressure.
- Reflex sight glasses – these have a prismatic groove on one side, which reflects and creates a contrast between the fluid and the background, making it easier to see. They commonly used in high-pressure applications.
- Transparent sight glasses – these are made of clear or glass and allow for a direct visual inspection of the fluid in the pipeline.
Codes and standards of pipe sight glasses
Pipe sight glasses are typically used in piping systems to provide visual indications of fluid level, flow, or color. Here are some common codes and standards that apply to pipe sight glasses: ASME B31.1, ASME B31.3, ASTM F2878, DIN 28120, ISO 10931 etc.
Introduction of pipe valve:
A pipe valve is a mechanical device used to regulate the flow of, gas, or oil through a pipeline. It is an essential component of the pipeline system, which is used for various industrial applications. They come in different types, designs, and sizes to cater to the specific needs of various industries.
Types of pipe valve:
There are several types of pipe valves including gate valves, ball valves, butterfly valves, globe valves, needle valves, and check valves
- Gate valves: These valves are used to control the flow of fluid by lowering and raising a metal gate that blocks the flow.
- Ball valves: These valves use a ball to regulate the flow of fluid, and they are primarily used for shut-off services.
- Butterfly valves: These valves control the flow of fluid by using a circular disc that is perpendicular to the flow axis inside the pipe.
- Globe valves: These valves control flow of fluid by using a disk that moves up and down to adjust the flow rate.
- Needle valves: These valves control the flow of fluid by using a tapered needle that fits a seat, reducing the flow rate.
- Check valves: These valves allow fluid flow in one direction only, preventing backflow.
Codes and standards of pipe valve:
Pipe valves are and manufactured in accordance with various standards and codes, such as ASTM, ANSI, API, ASME. These codes and standards ensure that the valves meet the required quality and safety standards in their respective industries.