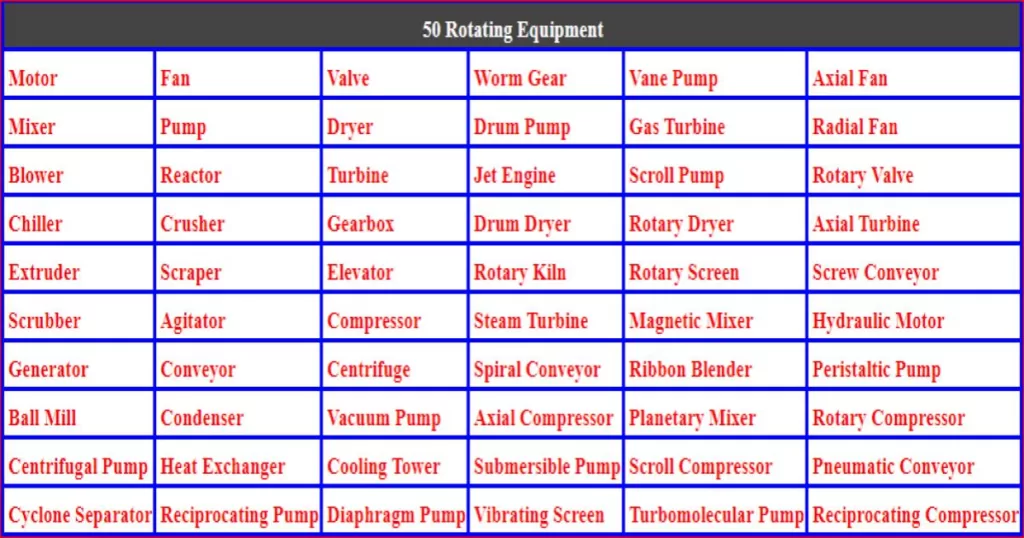
Preventive Maintenance (PM) plans
The frequency of preventive maintenance (PM) plans for industrial equipment varies depending on the type of equipment, its age, condition, and usage. Below are some common types of equipment used in chemical industries, their recommended PM frequencies, and a task list for each:
Pumps:
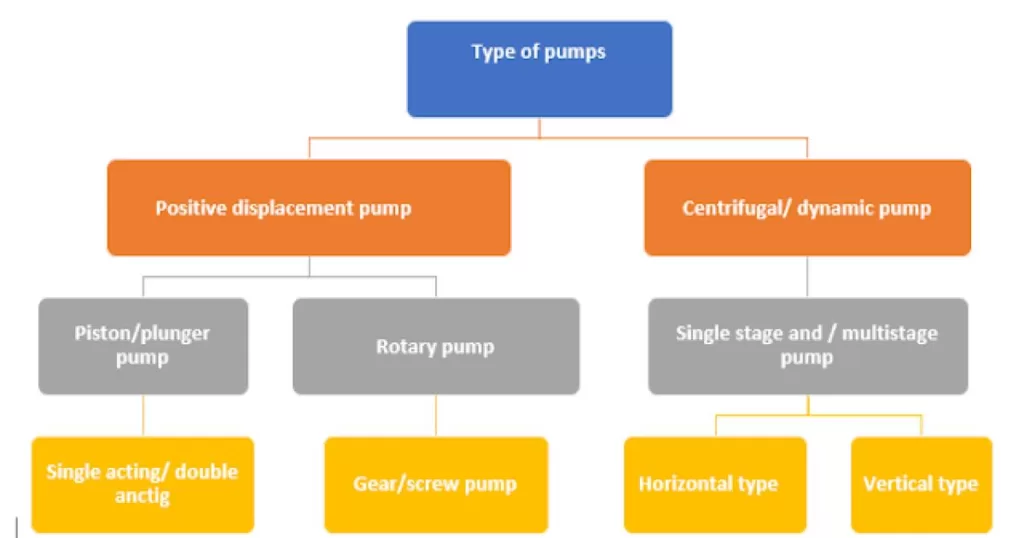
Pumps are devices that move fluids (liquids or gases) by mechanical action, typically converting electrical energy into hydraulic energy. Pumps can be classified by their method of displacement into positive-displacement pumps, dynamic pumps, and other.
Positive-displacement pumps use moving parts (such as pistons, gears, lobes, or diaphragms) to trap and displace a fixed amount of fluid with each cycle. They can produce high pressures and handle viscous fluids, but they need to be protected from overpressure and cavitation.
Dynamic pumps use rotating or oscillating parts (such as impellers, blades, or vanes) to impart kinetic energy and pressure to the fluid. They can handle large volumes and low viscosities, but they are sensitive to changes in flow and head14.
Other types of pumps include gravity pumps, steam pumps, valveless pumps, impulse pumps, velocity pumps, and special effect pumps. These pumps use different principles or mechanisms to move fluids, such as gravity, steam, valves, impulses, velocities, or special effects.
Pumps are widely used in various applications such as water supply, irrigation, drainage, sewage, firefighting, oil and gas production, chemical processing, power generation, heating and cooling systems, medical devices, and more
Daily tasks:
Check for leaks and abnormal noises or vibrations.
Monitor bearing temperatures and lubrication system pressures.
Check the impeller for any signs of damage.
Inspect the seal flush system for proper operation.
Check the alignment between the pump and the motor.
Monthly tasks:
Check and replace lubricating oil or grease.
Check the bearing condition and lubrication level.
Inspect the impeller for erosion, corrosion, or damage.
Clean the pump casing and impeller.
Check the vibration levels and make necessary adjustments.
Quarterly tasks:
Check the alignment between the pump and the motor.
Check the bearing condition and lubrication level.
Inspect the impeller clearance and adjust if necessary.
Check the seal faces and replace if necessary.
Check the volute and casing for corrosion, erosion, or damage.
Annual tasks:
Inspect and replace worn bearings, if needed.
Replace mechanical seals and gaskets.
Check the impeller balance and adjust if necessary.
Inspect the pump shaft for wear, bending, or damage.
Inspect and replace any worn or damaged parts.
Overhaul tasks:
Remove the pump from service.
Disassemble the pump and clean all parts.
Inspect all parts for wear, cracks, and damage.
Replace any worn or damaged parts.
Reassemble the pump, perform balancing, and conduct tests before returning it to service.
It is essential to note that the above task lists are general guidelines and the specific maintenance plan for a centrifugal between bearing pump should be determined by the manufacturer’s recommendations, industry standards, and the pump’s usage and condition. Regular inspection, preventive maintenance, and timely repairs can extend the life of the equipment and minimize downtime.

Centrifugal overhang Pumps:
inspection, maintenance plan, overhauls, with 10 task list Daily, Monthly, Quarterly, Annual. Centrifugal overhang pumps are critical equipment in industries such as oil and gas, chemical, and power generation. To keep them running efficiently, a comprehensive inspection and maintenance plan is essential. Below is a list of tasks for daily, monthly, quarterly, and annual maintenance of centrifugal overhang pumps:
Daily tasks:
Inspect the pump for any leaks, unusual noises, or vibrations.
Check the lubrication system for proper oil level and pressure.
Check the coupling alignment.
Check the motor bearings and lubrication.
Inspect the impeller for any signs of damage or erosion.
Monthly tasks:
Clean the pump casing and impeller.
Check the seal flush system for proper operation.
Check the seal faces for any signs of wear or damage.
Check the wear rings for any signs of wear.
Inspect the volute and casing for any signs of corrosion or erosion.
Quarterly tasks:
Check the impeller clearance and adjust if necessary.
Check the alignment between the pump and the motor.
Check the vibration levels and make any necessary adjustments.
Inspect the bearings for any signs of wear or damage.
Check the coupling bolts and tighten if necessary.
Annual tasks:
Replace the pump bearings.
Replace the mechanical seals.
Check the impeller balance and adjust if necessary.
Inspect the pump shaft and sleeves for any signs of wear.
Check the motor alignment and make any necessary adjustments.
Overhaul tasks:
Remove the pump from service.
Disassemble the pump.
Inspect all parts for any signs of wear or damage.
Replace any damaged or worn parts.
Reassemble the pump and perform all necessary tests before returning it to service.
It is important to note that the above task lists are general guidelines and the specific maintenance plan for a centrifugal overhang pump should be determined by the manufacturer’s recommendations, industry standards, and the pump’s usage and condition. Regular inspection, preventive maintenance, and timely repairs can extend the life of the equipment and minimize downtime.
Reciprocating Pumps:
inspection, maintenance plan, overhauls, with 10 task lists Daily, Monthly, Quarterly, Annual. Reciprocating pumps are commonly used in various industries, including oil and gas, chemical, and power generation. These pumps require regular inspection and maintenance to ensure they operate efficiently and reliably. Below is a list of tasks for daily, monthly, quarterly, and annual maintenance of reciprocating pumps:
Daily tasks:
Check for leaks and abnormal noises or vibrations.
Check the lubrication system for proper oil level and pressure.
Check the coupling alignment.
Inspect the pump rod for any signs of wear or damage.
Inspect the valves and valve seats for any signs of wear or damage.
Monthly tasks:
Clean the pump casing and valves.
Check the seal flush system for proper operation.
Check the packing for wear or damage.
Check the valve lift and adjust if necessary.
Check the suction and discharge pressure gauges for accuracy.
Quarterly tasks:
Check the valve clearance and adjust if necessary.
Check the pump rod run-out and alignment.
Check the pump foundation for any signs of settlement.
Check the packing and replace if necessary.
Check the valve springs for any signs of wear or fatigue.
Annual tasks:
Replace the pump valves.
Replace the packing and gaskets.
Inspect the pump cylinders and pistons for any signs of wear or damage.
Inspect the bearings for any signs of wear or damage.
Check the alignment between the pump and the motor.
Overhaul tasks:
Remove the pump from service.
Disassemble the pump and clean all parts.
Inspect all parts for wear, cracks, and damage.
Replace any worn or damaged parts.
Reassemble the pump, perform balancing, and conduct tests before returning it to service. It is important to note that the above task lists are general guidelines and the specific maintenance plan for a reciprocating pump should be determined by the manufacturer’s recommendations, industry standards, and the pump’s usage and condition. Regular inspection, preventive maintenance, and timely repairs can extend the life of the equipment and minimize downtime.
Screw Pumps:
inspection, maintenance plan, overhauls, with 10 task list Daily, Monthly, Quarterly, Annual. Screw pumps are positive displacement pumps that are commonly used in various industries, including oil and gas, chemical, and food processing. These pumps require regular inspection and maintenance to ensure they operate efficiently and reliably. Below is a list of tasks for daily, monthly, quarterly, and annual maintenance of screw pumps:
Daily tasks:
Check for leaks and abnormal noises or vibrations.
Check the lubrication system for proper oil level and pressure.
Check the coupling alignment.
Check the suction and discharge pressure gauges for accuracy.
Inspect the pump screws and casing for any signs of wear or damage.
Monthly tasks:
Clean the pump casing and screws.
Check the seal flush system for proper operation.
Check the bearing lubrication level and condition.
Check the suction and discharge valves for proper operation.
Check the torque of the screws.
Quarterly tasks:
Check the bearing condition and replace if necessary.
Check the pump casing and screws for any signs of erosion, corrosion, or damage.
Check the seal faces and replace if necessary.
Check the suction and discharge piping for any signs of wear or damage.
Check the suction strainer and clean if necessary.
Annual tasks:
Replace the pump screws and casing if necessary.
Replace the bearings and seals.
Check the alignment between the pump and the motor.
Inspect the drive belts and replace if necessary.
Check the gear reducer oil level and condition.
Overhaul tasks:
Remove the pump from service.
Disassemble the pump and clean all parts.
Inspect all parts for wear, cracks, and damage.
Replace any worn or damaged parts.
Reassemble the pump, perform balancing, and conduct tests before returning it to service. It is important to note that the above task lists are general guidelines and the specific maintenance plan for a screw pump should be determined by the manufacturer’s recommendations, industry standards, and the pump’s usage and condition. Regular inspection, preventive maintenance, and timely repairs can extend the life of the equipment and minimize downtime.
Reciprocating diaphragm Pumps:
Inspection, maintenance plan, overhauls, with 10 task list Daily, Monthly, Quarterly, Annual. Reciprocating diaphragm pumps are positive displacement pumps that are commonly used in various industries, including chemical processing, water treatment, and pharmaceuticals. These pumps require regular inspection and maintenance to ensure they operate efficiently and reliably. Below is a list of tasks for daily, monthly, quarterly, and annual maintenance of reciprocating diaphragm pumps:
Daily tasks:
Check for leaks and abnormal noises or vibrations.
Check the lubrication system for proper oil level and pressure.
Check the suction and discharge pressure gauges for accuracy.
Inspect the diaphragm for any signs of wear or damage.
Check the valve operation and adjust if necessary.
Monthly tasks:
Clean the pump and surrounding area.
Check the seal flush system for proper operation.
Check the diaphragm for any signs of fatigue or cracking.
Check the valve springs for proper tension.
Check the torque of the pump fasteners.
Quarterly tasks:
Check the piston rods and replace if necessary.
Check the diaphragm backup plates and replace if necessary.
Check the valve seats and replace if necessary.
Check the suction strainer and clean if necessary.
Inspect the air chamber for any signs of damage or wear.
Annual tasks:
Replace the diaphragm and backup plates.
Check the alignment between the pump and the motor.
Inspect the drive belts and replace if necessary.
Check the air chamber diaphragm for any signs of wear or damage.
Check the air compressor for proper operation.
Overhaul tasks:
Remove the pump from service.
Disassemble the pump and clean all parts.
Inspect all parts for wear, cracks, and damage.
Replace any worn or damaged parts.
Reassemble the pump, perform balancing, and conduct tests before returning it to service. It is important to note that the above task lists are general guidelines and the specific maintenance plan for a reciprocating diaphragm pump should be determined by the manufacturer’s recommendations, industry standards, and the pump’s usage and condition. Regular inspection, preventive maintenance, and timely repairs can extend the life of the equipment and minimize downtime.
Agitator gear box:
inspection, maintenance plan, overhauls, with 10 task list Daily, Monthly, Quarterly, Annual. Agitator gearboxes are important components in mixing systems used in various industries such as chemical processing, pharmaceuticals, and food production. Proper maintenance and inspection of these gearboxes are necessary to prevent equipment failure and ensure efficient operation. Here is a list of tasks for daily, monthly, quarterly, and annual maintenance of agitator gearboxes:
Daily tasks:
Check for any abnormal noises, leaks, or vibrations.
Check oil levels and temperatures.
Check for proper coupling alignment.
Check for any wear or damage on the gearbox, bearings, and seals.
Check for proper lubrication.
Monthly tasks:
Clean the gearbox and surrounding area.
Inspect and replace worn or damaged bearings and seals.
Inspect the gearbox for signs of wear or damage.
Check the alignment of the coupling and correct if necessary.
Check oil levels and temperatures.
Quarterly tasks:
Drain and replace the gearbox oil.
Inspect the gearbox for any signs of rust or corrosion.
Check and adjust the gear backlash.
Inspect and clean the breather filter.
Check the alignment of the gearbox and correct if necessary.
Annual tasks:
Perform a complete overhaul of the gearbox.
Inspect and replace any worn or damaged gears.
Inspect and replace worn or damaged seals.
Inspect and replace worn or damaged bearings.
Check the alignment of the gearbox and correct if necessary.
Overhaul tasks:
Remove the gearbox from service.
Disassemble the gearbox and clean all parts.
Inspect all parts for wear, cracks, and damage.
Replace any worn or damaged parts.
Reassemble the gearbox, perform balancing, and conduct tests before returning it to service. It is important to note that the above task lists are general guidelines, and the specific maintenance plan for an agitator gearbox should be determined by the manufacturer’s recommendations, industry standards, and the gearbox’s usage and condition. Regular inspection, preventive maintenance, and timely repairs can extend the life of the equipment and minimize downtime.