What are the gear couplings?
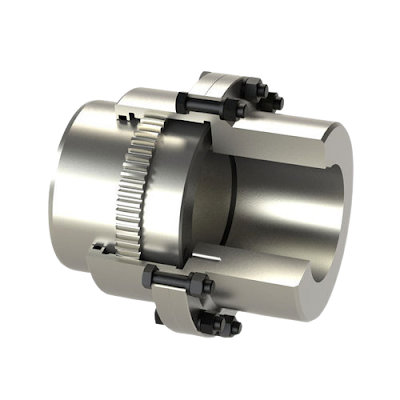
Gear coupling
Gear couplings are the type of flexible coupling and mostly use for high torque transmission for heavy machinery (positive displacement pump, gearbox, pump) and excess speed application as well. This type of coupling designed to transmit torque between two non-collinear equipment shafts, and with the help of two flexible joints. this couplings torque transmit capability is more with small size as compared to other couplings.
Gear couplings equipped with a seal, also easy to install, less downtime as compared to other types of coupling, this is mostly available with an interference fit between hub and equipment shaft, with their high torque transmission capacity and versatility used for high torque transmission application. The initial cost of c these couplings is very low.
To compensate for the misalignment, a backlash is given between both meshing gear, backlash is necessary for gear coupling. Backlash is a system that allows the meshing gear to free (very little) movement between each other during the condition of misalignment, and sudden buildup force of both equipment shaft and adjunct the same. But some standards need to be followed before the selection of a couple, like for the spacial purpose coupling standard API 671 (Flexible coupling) / ISO 10441.
- Each shaft hub (Flexible coupling) is balanced in accordance according to AGMA 9000.
- Flexible coupling keys and bore should be balanced in accordance according to AGMA 9000.
- For the special purpose application standard lubrication and shaft sealing API 614.
- Flexible coupling nomenclature standard will be followed according to AGMA 510.
Gear coupling parts name
Some of the important parts of these coupling are described below.
Sleeve with internal gear, coupling hub with external gear, connecting bolt, lubricants, o rings, gasket, lubrication plugs, shaft key, snap ring. Some of the other parts also could be used depends on the manufacturer.
To learn the full course on coupling click links as given with the title 👉👉👉👉👉👉
- What is coupling and types of coupling – Parts 1 👈👈👈
- Flexible coupling and types of flexible coupling – Parts 2 👈👈👈
- Rigid coupling and types of rigid coupling -Parts 3 👈👈👈
- Fluid coupling and what types of fluid coupling – Parts 4 👈👈👈
- Grid coupling and what types of grid coupling – Parts 5 👈👈👈
- gear coupling and types of gear coupling – Parts 6 👈👈👈
Which are the types of gear couplings?
A gear coupling is a type of flexible coupling because gear coupling can compensate for some amount of vibration, misalignment between equipment shaft, and damped shock load as well. It can also allow a little amount of angular misalignment between the driver and driven equipment shaft. But that will lead to increased backlash between meshing gear teeth and cause premature failure of couplings.
How do you choose a gear coupling?
The basic selection guide for gear coupling has been described below, and many more important factors are also described.
Identify the required torque transmission, required speed to operate, size of the coupling, services factor, maximum and minimum torque during operation, initial cost, maintenance interval, outside diameter, coupling materials, the weight of coupling hub, a moment of inertia, torsional stiffness, backlash, misalignment compensate capacity, DBSE (distance between shaft end), balancing required, lubrication and other and per requirement.
How do I know my coupling size?
If you want to know about your equipment size, there are two methods to find out the same. These are the following. Before discussing your equipment’s coupling size, you should have to require some measuring tools or devices to measure for the same. Like digital or analog vernier Caliper, bore gauge, a depth gauge to know about bore size and micrometer, etc.
First of all, if the coupling hubs are not installed, by the help of a bore gauge measure the bore of the shaft hub, then measure the length of each hub.
If the coupling hubs are installed, then check both equipment shaft OD outside diameter, and then measure the length as well. That can be also measured by the help outside the micrometer. To check the bore of the hub you can use a bore gauge, depth gauge, vernier caliper, and micrometer as well.
For example, to measure with the help of a vernier caliper, expand the tips of the vernier caliper jaw until they’re fully extended up to the hub size and note down the caliper current reading. This will give you the correct size coupling hub that you have too needed. And check the manufacturer catalog, match it with module numbers in the given booklet.
How does a gear coupling work?
The working principle of these coupling is the same as another flexible coupling, it is designed to transmit high torque with high and low RPM. And it falls in the category of flexible coupling, and the assembly of gear coupling has two flexible joints with a sleeve with an internal gear. When driver equipment starts to rotate, then the same driven equipment also starts rotates because is directly connected with the help of inside or outside gear tooth sleeve.
What are the types of gear coupling?
There are many types of these coupling available in the market, some of the common types of gear coupling given below.
- Full Gear type
- Half Gear Half Rigid type
What is the difference between full gear and half gear coupling?
Full Gear type Coupling
In this type of coupling, the gear tooth formed on both hubs of equipment. It means that the driver and driven side hub have toothed, and both are connected by the inside tooth gear sleeve at both ends. And that will be connected by mesh the gear to each other. It can be compensating parallel and angular misalignment with little shaft float capacity.
Half Gear type Coupling
Half Gear type Coupling is working the same as full type gear coupling, but it is used with one toothed (flexible joint) and a rigid hub at each piece of equipment. The toothed coupling hub used with the driven side of the system, whereas the rigid flange hub use on the driver side, and both are connected with an internal toothed sleeve which is meshed with the toothed end and tighten bolted with the driver flanges hub.
What are the applications of gear couplings?
The main application of these coupling is like as, this is used for large size of the equipment and more torque transmission required, like a pump, compressor, turbine gearbox, conveyors, etc. And it can be easily installed and dismantle as well.
What are the reasons for gear coupling failures?
Gear coupling failures
- Both types of equipment are not aligning with each other properly (more misalignment)
- Not properly design and selection
- Backlash more between both equipment hubs.
- Excessive vibration between both equipment.
- Approx. 75% of gear coupling failure causes poor lubrication.
- Preventive maintenance is not done regularly.
- Additives, foreign particles, and impurities present in the lubricant.
- Not select appropriate lubricant and not change as per requirement.
- Approx 20% of failure due to improper alignment of a gear coupling.
- Wear particles increase from time to time due to misalignment.
What is the advantage of gear coupling?
- The advantages of gear type are more some of them given as below.
- High torques transmission and Low maintenance cost.
- Less downtime and Simple construction
- Only lubrication needed to replace during Preventive maintenance.
- Less space is required to install.
- Compensate little misalignment.
- Absorb shocks and vibrations
- Due to simple construction easily assembled or dismantled.
What does the number of gear coupling indicate?
The printed number for gear coupling indicates its size, specification, working speed and torque rang according to manufacture for that particular coupling. That will be suitable for the specific range of operation.
Why high-temperature heat on gear coupling is the problem?
The gear coupling is used in a wide variety of applications with its advantages, but new design gear coupling is specifically engineered to meet the high-temperature demands and other special needs of the industry with proper lubrication.
these coupling will fail as conventional O-ring seals are provided with ordinary gear. Couplings simply cannot stand up to the high temperatures common in many applications.
if coupling will work at a high temperature for a long time, which is not for the same, then seals become hard and brittle and start to dissolve with lubricants. Causing the lubricant to become contaminated and the coupling fails because the properties and viscosity of that oil have changed. So The traditional solution to this problem has been to use a metal Labyrinth seal with the latest coupling.
These metal seals can withstand high temperatures, but they are expensive, often doubling the cost of the coupling of total coupling. However, for the selection of these coupling to the steel mill, equipment coupling should withstand high temperatures.
Gear type coupling seal material
Point contact seal constructed from a fluorocarbon material. Similar to Teflon, Viton seals are capable of withstanding, continuous temperatures of 400 degrees Fahrenheit and intermittent temperatures of 600 degrees Fahrenheit. Viton seals are less expensive than metal seals. As a result, the Lifeline of steel mill equipment couplings can meet all the requirements of the steel industry and save approx 40 to 60 percent cost at the same size.
If couplings are equipped with a metal seal for high temperature. Allows easy infield adjustment for axial positioning of existing machinery with gap variances. Manufacture follow AGMA 9000 standard, for all steel mill gear couplings.
Grease has been used to increase the Lifeline of steel mill gear couplings. They can run three years before requiring any lubrication. Available from stock in sizes double engagement, single engagement spacer, and floating shaft types.