What is Hydro Test For Pipe Line?
Hydro test is a technique to identify the defect part or location of the equipment. It is mostly used for leakage checking methods for piping and pipeline networks. There are two types of detection techniques used for leakage detection; these are hydraulic and pneumatic tests. Hydro Testing general requirements and criteria explained for process pipeline under specification code ASME B31.3 Section 345.4.1.
The test fluid shall be water otherwise there is always the possibility of damage to the equipment with other fluids due to freezing. And water will cause adverse effects on the piping. Some special cases suitable compatible non toxic liquid may be used as per user convenience. But if the hydro test fluid is flammable than its flash point is at least 49°C (120°F). This type of pressure test should be performed at a safe location.

In ASME B31.3 Section 345.4.2 specified the hydrostatic test pressure at any part in a metallic pipeline shall be as follows:
- At least 11⁄2 times of the design pressure for the applicable system.
- Design temperature shall be above the test temperature and minimum test pressure shall be calculated by Eq.
- Pr = (1.5 x P x Sr) / S, except that the ratio of ST/S shall not exceed 6.5
where ST = stress at test temp, S = stress at design temp (see Table A-1 of ASME B31.3), P = design gauge pressure, PT = minimum test gauge pressure.
In some cases defined hydro test pressure produces a nominal or longitudinal pressure stress in excess of the yield strength at hydro test temperature. Hydro test pressure may be reduced up to the maximum pressure that will not exceed the yield strength at hydro test temperature.
If in the scenario of Hydrostatic test to be performed Piping With Vessels as a complete close system fluid test pressure of piping attached to a vessel shall be the same as or less than the test pressure for the vessel, the piping may be tested with the vessel at the piping test pressure.
If where the test pressure of the piping is more than the vessel test pressure, and practically it is not possible to isolate the piping from the vessel, then the piping and vessel shall be tested together at the vessel test pressure prior to take the owner approvals and Defined vessel test pressure should not be less than 77% of the piping test pressure. That will be calculated in accordance with ASME B31.3 para. 345.4.2(b).
Preparation for Hydro Tests
Prior to starting any leakage tests like hydrostatic and pneumatic, All piping or pipeline networks connected equipment must be prepared for leakage tests. ASME B31.3 has created guidelines for test preparation like Piping, drains, vents, pressure relieving devices, discharge pipe, sewers, and seal drum stack downstream shall not be needed for the pressure test.
Compare PID and Isometric Drawing
Match all vent, drain, and other types of equipment properly before they perform the hydro test. All radiographic and ultrasonic inspections should be completed and approved by the QC team before performing pressure tests. Conducting radiography of all the weld joints as defined by QC and design team such as 20% or 80% or maybe 100% of weld joints. And it is the execution engineer’s responsibility to ensure that radiography / ultrasonic inspection shall also not be waived off if the pipeline is to be hydrostatically tested.
Joints shall be exposed
As per ASME B31.3 Guideline in Section 345.3.1 pipeline all weld joints, including structural welds to pressure-containing components like stiffener shall not be insulated and open for examination during leak testing, except that joints are prior tested in accordance with ASME Code. All joints may not be painted prior to hydro testing unless a sensitive leak test (para. 345.8) is required.
Provision of Temporary Supports
According to ASME B31.3 Section 345.3.2 in case of hydro test performing on the vapor or gas pipeline, additional temporary supports shall be provided if required to sustain the weight of test liquid because test liquid is heavier than gas and that pipeline is designed for gas only.
Spring Supports in Piping System
All spring supports shall be in cold condition (locked without any pipeline loads) or could be removed during the period of hydro testing. The Piping which are supported by spring or counterweight locked up temporarily to a degree sufficient to take the weight of the test fluid. And locked pins shall not be removed from spring supports til testing is not completed and drain the fluid and then get clearance for the inspection team. Make sure and avoid overloading any parts of the spring support and structures during testing.
Piping with Expansion Joints
According to ASME B31.3 following criteria shall apply when an expansion joint is provided in the piping system for leakage test.
Expansion joints which depend on external main anchors to hold back the pressure at end load shall be tested in place in the installed pipeline. A self-hold back expansion joint shall be tested at the fabrication shop or shall be isolated from the system during test, except that such expansion joints shall be installed in the piping system when a sensitive leak test is performed, in accordance with para. 345.8 is required.
A piping system with incorporation of expansion joints shall be leak tested without temporary joint or anchor hold back at the lesser of 1.5 times of design pressure for a bellows-type expansion joint. The system test pressure is governed in accordance with ASME B31.3 para 345. In case shall a bellows-type expansion joint be subjected to a test pressure greater than the manufacturer’s test pressure? When a system leaks a test at a pressure greater than the minimum test pressure specified in or greater than 1.5 times of the design pressure within the limitations of para. 345.2.1(a) is required, bellows-type expansion joints shall be removed from the piping system or temporary holdback shall be added to limit main anchor loads if necessary.
Limits of Tested Piping
According to ASME B31.3 Section 345.3.4 if equipment is connected with a piping system, it shall be either disconnected or isolated by blinds from the piping system. A valve may also be used (including its closure mechanism) which is suitable for the sustain of the test pressure.
Rotary Machinery
For rotating equipment like pumps, turbines, and compressors, lube and seal oil systems which could be damaged or malfunctioned by water. These systems shall not be subjected to the piping test pressure.
Temporary Spades and Blanks
All temporary spades and blanks which are installed for testing purposes only shall be designed to withstand the test pressure without any distortion. Installation of spades or blinds shall be clearly visible during testing. The standard practice is to use blind flanges as per ASME B16.5 or B16.47 and spades shall be in accordance. to ASME B16.48.
Check Valves
All check valves which are installed in the system shall be removed prior to testing, where pressure can not be located on the upstream side of the valve. The locking device of the flap pivot pin shall be reinstalled together with the flap and a new cover gasket shall be installed after completion of the test.
Completion of Hot Work
Before starting, a hydrostatic test of all hot work activity should have been completed on a piping system. Any types of hot work include related to hot work like welding, cutting, grinding or the post weld heat treatment (PWHT).
Installation of Barriers
Prior to pressurizing the pipeline system for testing, a hard barricade should be fixed around the piping system and fixed the sing board so people can easily identify pressure hazard areas. Public address. Announcements are also to be made and access restriction procedures such as work permit are implemented. Under these circumstances, anyone other than an authorized person shall not be allowed within the safety barriers.
Control Valves
Control Valves and soft-seal block Valves shall be dismantled or removed from the piping prior to the test and replaced with pipe spools.
Physical Inspection and Check for the following:
- All flanges shall be completely tightened and torqued flanges without missing bolts or gaskets.
- All gravity supports were installed and the pipeline rested on it.
- Proper pipe routing without any deviation.
- Dismantle all valves, instrumentation equipment, strainer and non return valve..
- All vents and drains shall be installed to allow proper filling and draining
- Color coding is used properly used for all material types and verified using color codes or markings, and heat numbers recorded.
- All required piping stress relief, weld examinations, and welding documentation completed and acceptable.
Testing Documentation Requirements
The individual system documentation i.e. test pack shall be available prior to any testing and shall be mentioned information like test limits, test pressure, test medium, duration, test blinds, blind flanges, vents and drains. Always should use of marked up P&Ids coupled with isolation registers should be utilized to identify the locations of blinds, valve drops, vents and drains.
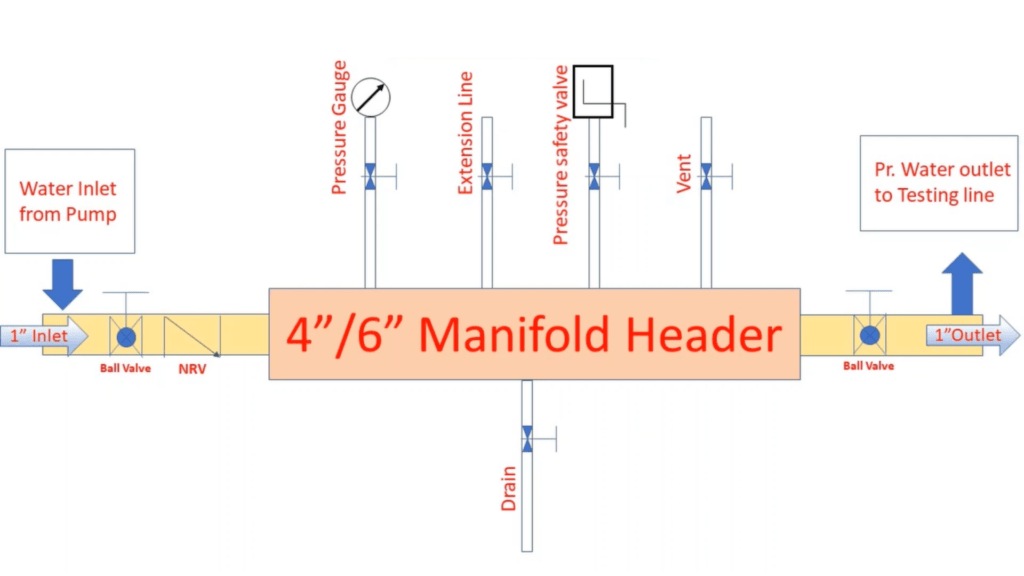
Testing Equipment
All hydro test equipment such as pumps, manifolds, pressure and temperature recorders, pressure gauges should be calibrated, tested, and connected to the lowest convenient connection within the system to ensure best results.